Introduction
In the annals of history, few events have shaped the course of nations as profoundly as World War 2. This global conflict, spanning from 1939 to 1945, reshaped political landscapes, economies, and societies across the globe. But what were the driving forces behind this cataclysmic event? In this comprehensive exploration, we will dissect the intricate web of causes that led to World War 2, shedding light on the historical context and the consequences that reverberate through time.
Why Did World War 2 Start?
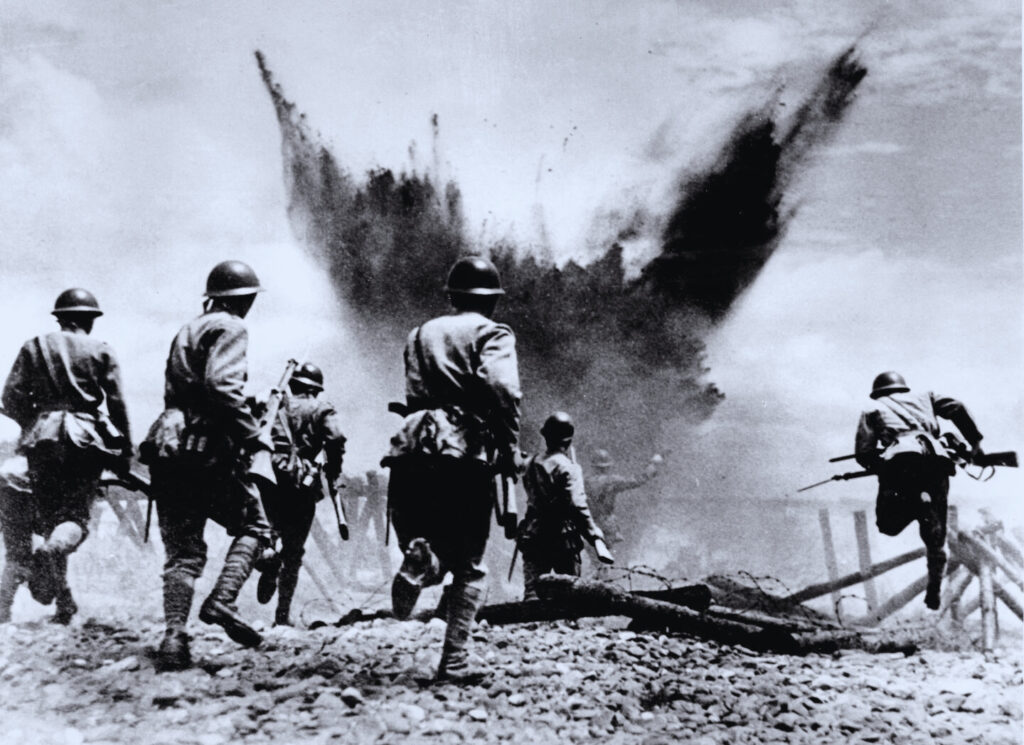

World War 2, often referred to as the most devastating conflict in human history, originated from a complex interplay of political, economic, and social factors. The aftermath of World War 1, marked by economic instability, territorial disputes, and unresolved animosities, set the stage for the rise of totalitarian regimes and aggressive expansionism. The relentless pursuit of power and resources by these regimes, coupled with a failure of international diplomacy, culminated in the outbreak of World War 2.
The Rise of Totalitarian Regimes
The Seeds of Fascism
The 1920s and 1930s witnessed the rise of fascist ideologies in Italy, led by Benito Mussolini, and in Germany, under the charismatic leadership of Adolf Hitler. These dictatorial regimes promoted ultra-nationalism, militarism, and racial superiority, sowing the seeds of discontent and aggression.
Hitler’s Expansionist Ambitions
Adolf Hitler’s aggressive expansionist policies, driven by a desire to establish a Greater German Empire, led to the annexation of Austria in 1938 and the subsequent invasion of Czechoslovakia. These actions met with limited resistance from the international community, emboldened Hitler to pursue further territorial gains.
Global Economic Instability
The Great Depression
The world was reeling from the Great Depression, a severe economic downturn that crippled economies and left millions unemployed. Nations struggled to recover, fostering a climate of desperation and uncertainty, making them susceptible to extremist ideologies promising solutions to their plight.
Competing Economic Interests
Economic disparities and competition for scarce resources exacerbated tensions among nations. Trade barriers, protectionist policies, and economic nationalism further strained international relations, creating an environment ripe for conflict.
Failure of International Diplomacy
Appeasement Policies
In the face of escalating aggressions, some Western powers adopted appeasement policies, hoping to avoid another devastating war. However, these policies only emboldened aggressor nations, allowing them to push boundaries and test the limits of international tolerance.
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, a non-aggression agreement between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, stunned the world. This pact, while providing a reprieve for Germany, paved the way for further territorial conquests, ultimately leading to the invasion of Poland in 1939.
Consequences of World War 2
The repercussions of World War 2 were profound and far-reaching. The war led to unprecedented human suffering, loss of life, and widespread destruction. The establishment of the United Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future global conflicts, was a direct response to the horrors of World War 2.
Technological Advancements
The war spurred significant technological advancements, particularly in aviation and nuclear science. These innovations, born out of wartime necessity, laid the foundation for subsequent advancements, shaping the modern world.
Redrawing of National Borders
The post-war era witnessed the redrawing of national borders and the decolonization of several nations. The emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers marked the beginning of the Cold War, a period of ideological and geopolitical rivalry that defined global politics for decades.
Conclusion
In unraveling the complex tapestry of events that led to World War 2, it becomes evident that a combination of political ideologies, economic challenges, and diplomatic failures paved the way for this global conflict. The consequences of the war were profound, shaping the world in ways that continue to influence our lives today. As we reflect on the lessons of history, it is crucial to understand the intricate factors that led to World War 2, ensuring that such a devastating conflict is never repeated.
Read also: Why Did Mendel Choose Pea Plants? The Father of Genetics
Frequently Asked Questions
Why did World War 2 start?
World War 2 began due to a complex interplay of factors, including the rise of totalitarian regimes, global economic instability, and the failure of international diplomacy. These factors created a volatile environment, eventually leading to the outbreak of the war in 1939.
What were the key events that led to World War 2?
Key events include the aggressive expansionist policies of Nazi Germany, the Great Depression, appeasement policies by Western powers, and the signing of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union. These events heightened tensions and set the stage for the conflict.
How did World War 2 impact the world?
World War 2 resulted in immense human suffering, technological advancements, and the redrawing of national borders. It led to the establishment of the United Nations and the beginning of the Cold War, shaping the political, social, and economic landscape of the post-war world.
Were there attempts to prevent World War 2?
Efforts to prevent the war included appeasement policies and diplomatic negotiations. However, these attempts were largely unsuccessful due to the aggressive expansionist agendas of totalitarian regimes and the deep-rooted economic and political challenges faced by nations at the time.
What role did the Great Depression play in the lead-up to World War 2?
The Great Depression created economic hardships and widespread unemployment, fostering a climate of desperation. This economic instability made nations susceptible to extremist ideologies, leading to the rise of totalitarian regimes and aggressive expansionist policies, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of World War 2.
How did World War 2 impact technological advancements?
The demands of wartime production led to significant advancements in technology, particularly in aviation and nuclear science. These innovations, driven by the need for military superiority, laid the groundwork for subsequent scientific progress, shaping the modern world.