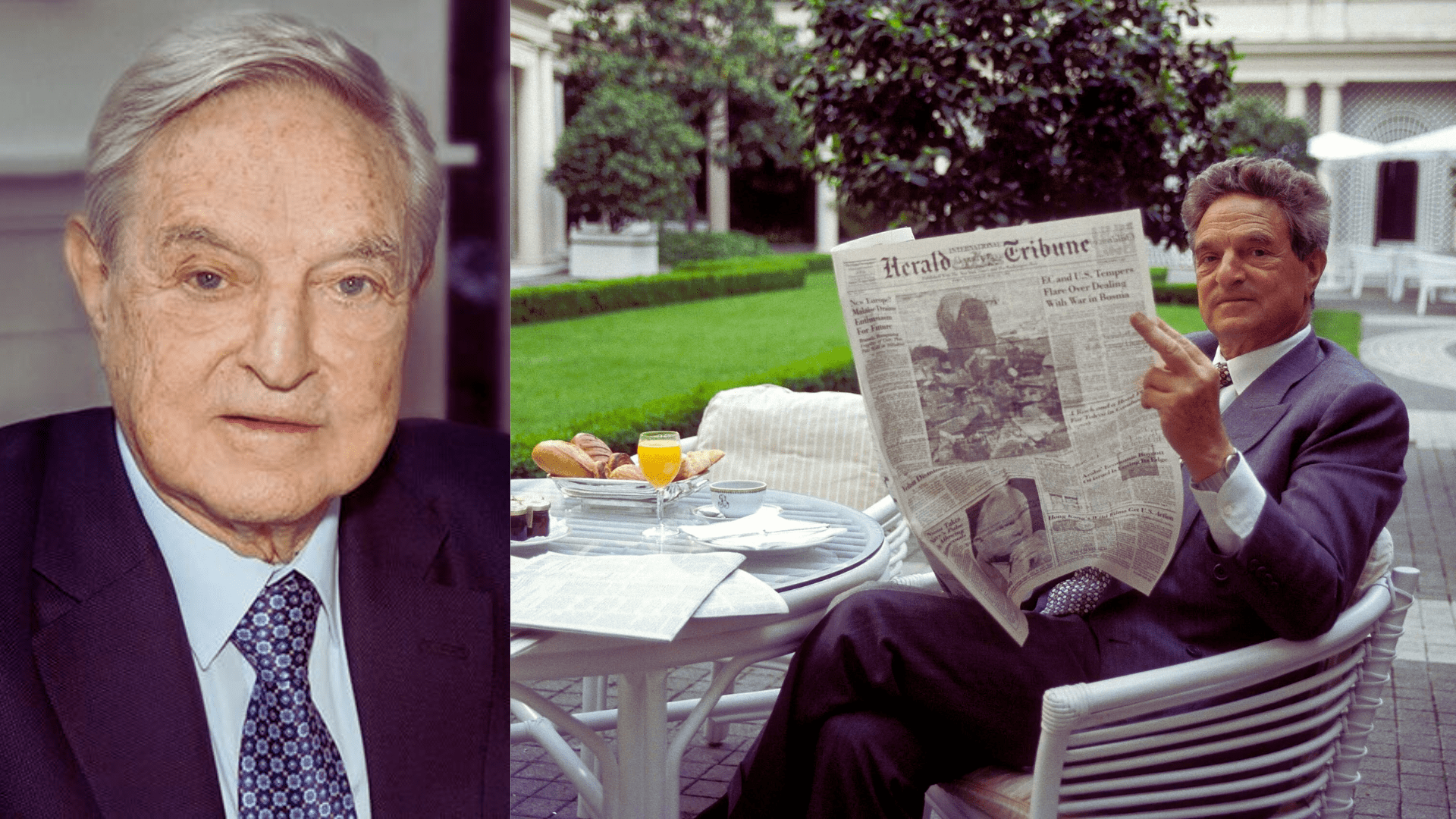
George Soros, born on August 12, 1930, in Budapest, Hungary, is a renowned Hungarian-American billionaire, hedge fund manager, and philanthropist. Soros survived the Nazi occupation during World War II and later emigrated to England. He studied philosophy under Karl Popper at the London School of Economics (LSE) but decided against a career in philosophy, opting instead for finance. He began his financial career in London before moving to New York City, where he established Soros Fund Management in 1970.
Soros is known for his profound impact on global financial markets, particularly highlighted by his famous bet against the British pound in 1992. As of October 2023, Soros’s net worth was estimated at $6.7 billion. Beyond finance, Soros is one of the world’s foremost philanthropists, having donated over $32 billion to various causes through the Open Society Foundations, which operate in over 100 countries promoting human rights, democratic governance, and access to education and health care.
Early Life and Education
Birth and Origins
George Soros was born on August 12, 1930, in Budapest, Hungary, into a non-observant Jewish family. During his early life, Soros lived through the harrowing times of the Nazi occupation of Hungary in 1944–1945, a period during which over 500,000 Hungarian Jews were murdered. Despite these challenges, his family survived, and Soros later emigrated from Hungary to the United Kingdom in 1947. He pursued his education at the London School of Economics before moving to the United States, where he would eventually establish himself as a prominent financier and philanthropist.
Academic Journey
George Soros’s academic pursuits were concentrated at the London School of Economics (LSE). He enrolled in LSE, where he studied philosophy under Karl Popper, a renowned philosopher. Soros was deeply influenced by Popper’s ideas, particularly the concept of the “open society,” which would later shape much of his philosophical and philanthropic outlook. He earned a Bachelor of Science in philosophy in 1951, followed by a Master of Science in philosophy in 1954.
Soros’s Financial Career
The Beginning of a Tycoon
George Soros began his illustrious career in the finance industry by founding his first hedge fund, Double Eagle, in 1969. This initial venture proved successful and laid the foundation for his future in finance. Using the profits from Double Eagle, Soros established Soros Fund Management in 1973. That same year, he also founded Quantum Fund, which would grow to become the world’s largest hedge fund. Soros’s approach in these early years involved the application of his deep philosophical insights into market dynamics, which he referred to as the ‘alchemy’ of finance.
Major Financial Moves
George Soros is renowned for his investment strategies that capitalize on macroeconomic trends and market inefficiencies. His major financial strategies include:
- Exploiting Market Inefficiencies: Soros often seeks opportunities where market perceptions do not align with the underlying realities, thereby profiting from eventual corrections.
- Risk Management through Swift Action: A key aspect of Soros’s strategy involves the rapid recognition of mistakes and taking decisive action to rectify them, thus managing risk and capitalizing on opportunities as they arise.
- Theory of Reflexivity: This theory plays a central role in his financial practices, suggesting that market values are often driven by the fallible perceptions of participants, which in turn influence the fundamentals that are supposed to be reflecting.
Major Trades:
- Black Wednesday (1992): Perhaps his most famous trade, Soros speculated against the British Pound, foreseeing that it was overvalued against the Deutschmark. His fund famously ‘broke the Bank of England’ by betting against the pound, earning Soros an estimated $1 billion in profit from this trade alone.
Soros’s strategies and his significant trades highlight his philosophy of being a very active participant in the markets, using sophisticated financial instruments and a deep understanding of global economic trends to guide his investments.
Political Influence
Political Contributions
George Soros is a well-known political donor, predominantly supporting Democratic causes and candidates in the United States. Here are some key points about his political contributions:
- Significant Donations to Political Causes: Soros has financed various politically charged groups, especially around election times. For example, in 2021, a Soros-backed nonprofit contributed approximately $140 million to political groups in the buildup to the 2022 midterm elections.
- Support for Democratic Initiatives: His contributions often align with Democratic policies and initiatives. In recent times, Soros has funded efforts aiming to impact significant political changes, such as turning Texas blue through strategic political action committees influenced by Democratic campaigns.
These contributions underscore Soros’s influence in U.S. politics, particularly in supporting progressive and liberal agendas.
Impact on Global Politics
George Soros has significantly impacted global politics through his philanthropic activities, primarily through the Open Society Foundations. Here are some of the ways he has influenced global policies:
- Support for Democracy and Human Rights: Soros has been a staunch supporter of democratic ideals and human rights across the globe. His foundations have funded numerous initiatives aimed at promoting these values and influencing policy decisions and democratic processes in various countries.
- Financial Contributions to Policy-Shaping Entities: By providing substantial funding to organizations that support open society ideals, Soros helps shape policy debates and political landscapes. His support extends to causes that advocate for social justice and reform, contributing to a reshaping of political priorities and practices internationally.
- Public Advocacy and Literature: Soros has also used his public platform to advocate for changes in global financial and political systems, arguing that the existing structures often oppose the open society framework he champions. His books and public speeches provide a theoretical foundation that influences global political discourse.
Philanthropic Efforts
Foundations and Charities
George Soros has channeled his philanthropic efforts through several avenues, primarily through his establishment, the Open Society Foundations (OSF). Here are some key aspects of his contributions to various foundations and charities:
- Open Society Foundations (OSF): Founded by Soros in 1979, OSF aims to promote democratic governance, human rights, and economic, legal, and social reform. Its activities are widespread across the globe, providing support through grants, scholarships, and funding for civil society groups.
- Support for Education and Policy Change: Early philanthropic activities included funding scholarships for Black African university students. Over the years, this has expanded to support a broad range of educational, social, and legal initiatives worldwide, influencing policy and educational frameworks.
- Political and Social Contributions: Soros’s nonprofit has also made significant financial contributions to political groups and charitable organizations aligned with various causes, including progressive social policies such as abortion rights and same-sex marriage.
The Open Society Foundations
The Open Society Foundations (OSF), established by George Soros, stand as a pivotal part of his philanthropic legacy. Soros initiated his philanthropic activities in 1979, and OSF embodies his commitment to fighting for open societies globally. Here are some key points about OSF:
- Foundation and Mission: OSF was founded by George Soros with the mission to build vibrant and tolerant democracies whose governments are accountable to their citizens.
- Major Contributions: Soros has contributed more than $32 billion to the OSF, making it one of the largest philanthropic organizations focused on social justice.
- Global Impact and Focus Areas: The Foundations’ work is global, emphasizing justice, equity, freedom of expression, and climate justice as integral elements necessary for open societies.
- Historical Initiatives: The first international OSF was established in Hungary in 1984, focusing on educational exchanges that promoted free societies, which highlights Soros’s long-term commitment to education and free speech.
Controversies and Criticisms
Criticism in the Financial Sector
George Soros has faced several criticisms related to his activities and theories in the financial sector:
- “Breaking the Bank of England”: Soros is famously known for his role in “Black Wednesday” on September 16, 1992, when his massive short selling of the British pound forced the Bank of England to devalue the currency and exit the European Exchange Rate Mechanism. This event led to significant financial turmoil in the UK.
- Criticism of BlackRock’s Investments in China: Soros has criticized BlackRock’s investment initiatives in China, labeling them a “tragic mistake” that could potentially harm U.S. national security interests.
- Theory of Reflexivity: Soros has proposed the “Theory of Reflexivity” which argues that financial markets do not tend towards equilibrium and are influenced more by the perceptions of participants than external realities. This theory has been subject to debate and criticism within economic circles for its perceived departure from traditional market theories which emphasize equilibrium and external shocks.
Political Backlash
George Soros has faced significant political backlash primarily due to his philanthropic support for progressive causes and his high-profile political donations. The key aspects of the political controversies surrounding him include:
- Conspiracy Theories: Soros’s support for progressive causes and advocacy for open societies has made him a frequent target of conspiracy theories. These often portray him as a secretive power broker manipulating global politics, particularly criticized by right-wing groups.
- Blame in Political Narratives: His role in funding progressive movements and district attorney races in the U.S. has positioned him at the center of many right-wing conspiracy theories. These narratives accuse him of undermining traditional values and promoting a leftist agenda.
- Cultural and Political Impact: Soros’s philanthropy and political engagement have made him a polarizing figure, often criticized by political opponents who see his funding strategies as attempts to shape global politics to his views.
Legacy and Future Outlook
Contributions to Finance
George Soros’s impact on the financial world is profound and multifaceted, encompassing his investment strategies, market philosophies, and significant contributions to economic theory:
- Innovative Investment Strategies: Soros is widely recognized for his role in the world of finance, particularly through his hedge fund management that led to significant market successes, most famously his bet against the British pound in 1992, which earned him substantial profits and the nickname “The Man Who Broke the Bank of England”.
- Philosophical Contributions: His book, “The Alchemy of Finance,” discusses his theory of reflexivity, which has influenced economic thinking. This theory critiques traditional economic assumptions and highlights the impact of the cognitive functions of participants on market valuations.
- Philanthropic Investments: Beyond direct financial market impact, Soros has utilized his wealth to drive large-scale change in economic policy and development through his philanthropy. His donations have supported initiatives aimed at reducing poverty and encouraging open societies, thus indirectly influencing economic models and policies on a global scale.
Philanthropic Legacy
George Soros’s philanthropic legacy is marked by a profound dedication to advancing global human rights, freedom, and justice. Here are key aspects of his enduring influence through charity:
- Extensive Contributions: Soros has donated over $32 billion of his fortune to fund the Open Society Foundations, aiming to build vibrant and inclusive democracies whose governments are accountable to their citizens.
- Foundational Impact: Since 1979, his philanthropic efforts have focused on promoting justice, education, public health, and independent media across the world, reflecting his commitment to fighting the world’s most intractable problems.
- Visionary Approach: His unique approach to philanthropy includes addressing causes of poverty and discrimination by supporting civil society groups in more than 120 countries, including major initiatives for reform in his native Hungary and Eastern Europe during the Cold War.
- Leadership Transition: Recently, Soros began transferring leadership of his philanthropic activities to his son, ensuring the sustainability and continuity of his vision for global change and democratic openness.
Conclusion
George Soros’s life is a testament to the power of resilience and the impact one individual can have on the world. Whether viewed as a benefactor or a manipulator, Soros’s influence across finance, politics, and philanthropy is undeniable. His story offers valuable insights into the intersections of wealth, power, and responsibility.
Read also: What is Sully?