In the realm of time, change is inevitable. As the seasons shift and daylight waxes and wanes, our clocks bear witness to this eternal dance. One of the most anticipated and often misunderstood events in the realm of timekeeping is the daylight saving time change. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this phenomenon, exploring the reasons behind it, its global variations, and its impact on our lives.
Understanding the Concept of Daylight Saving Time (DST)
1. The Origin of Daylight Saving Time
The concept of Daylight Saving Time (DST) can be traced back to the early 20th century. The idea was first proposed by Sir Benjamin Franklin in 1784 but was not widely adopted until World War I. The primary objective was to conserve energy during the war by maximizing the use of daylight.
Benjamin Franklin’s Proposal
Benjamin Franklin, a renowned American inventor, and statesman, suggested the idea of adjusting clocks to save candlelight usage. He famously wrote a satirical letter to the Journal of Paris in 1784, proposing that Parisians could economize candle usage by waking up earlier to make use of natural sunlight.
World War I and Standardization

During World War I, several countries, including Germany and the United Kingdom, implemented DST to save fuel and energy resources for the war effort. The practice was also adopted in the United States as a wartime measure. However, after the war, there was no standardization, and different countries and regions continued to adjust their clocks independently.
Uniform Adoption and Modern Standardization

It was not until the mid-20th century that the adoption of DST became more uniform. In the 1960s, many countries established standardized start and end dates for DST to minimize confusion, making it easier for people to adjust their schedules.
In the United States, the Uniform Time Act of 1966 defined the start and end dates of DST, which were later amended in the Energy Policy Act of 2005 to extend the duration of DST, beginning on the second Sunday in March and ending on the first Sunday in November.
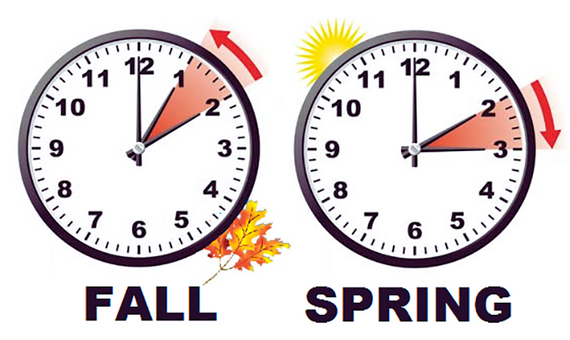
Today, the practice of moving the clocks forward in spring and backward in fall is a common ritual in many countries, allowing people to make the most out of the longer daylight hours during the warmer seasons.
2. How Daylight Saving Time Works
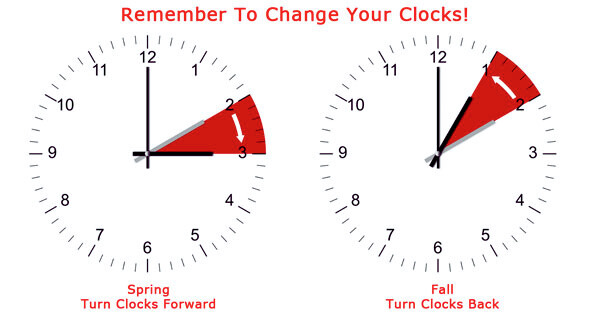
Daylight Saving Time (DST) is a practice where clocks are set forward by one hour during the warmer months to extend evening daylight. This adjustment is typically made in spring and reversed in fall, allowing people to make better use of natural daylight in the evenings. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DST works:
Clock Adjustment:

At the designated start date of DST, usually in spring, clocks are adjusted forward by one hour. For example, if the clock reads 2:00 AM, it is adjusted to 3:00 AM. This shift effectively moves an hour of daylight from the morning to the evening.
Purpose of DST:
- Maximizing Daylight: DST aims to make better use of daylight during the longer days of spring, summer, and early fall. By shifting an hour of daylight from the morning when many people are still asleep to the evening, individuals can enjoy more daylight after work or school.
- Energy Conservation: The primary objective behind DST is energy conservation. By extending evening daylight, people reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating in the evenings. This results in energy savings, especially in regions where there are distinct seasonal changes in daylight length.
Duration of DST:
DST typically lasts for several months, usually from spring to fall. The specific start and end dates can vary by country or region. The duration is carefully chosen to coincide with the period of the year when daylight is naturally longer, ensuring maximum benefit.
Clock Reversion:
At the end of the DST period, usually in the fall, clocks are adjusted back by one hour. For example, if the clock reads 2:00 AM DST, it is adjusted back to 1:00 AM standard time. This reversion returns the time to its standard schedule.
Adjustment Impact:
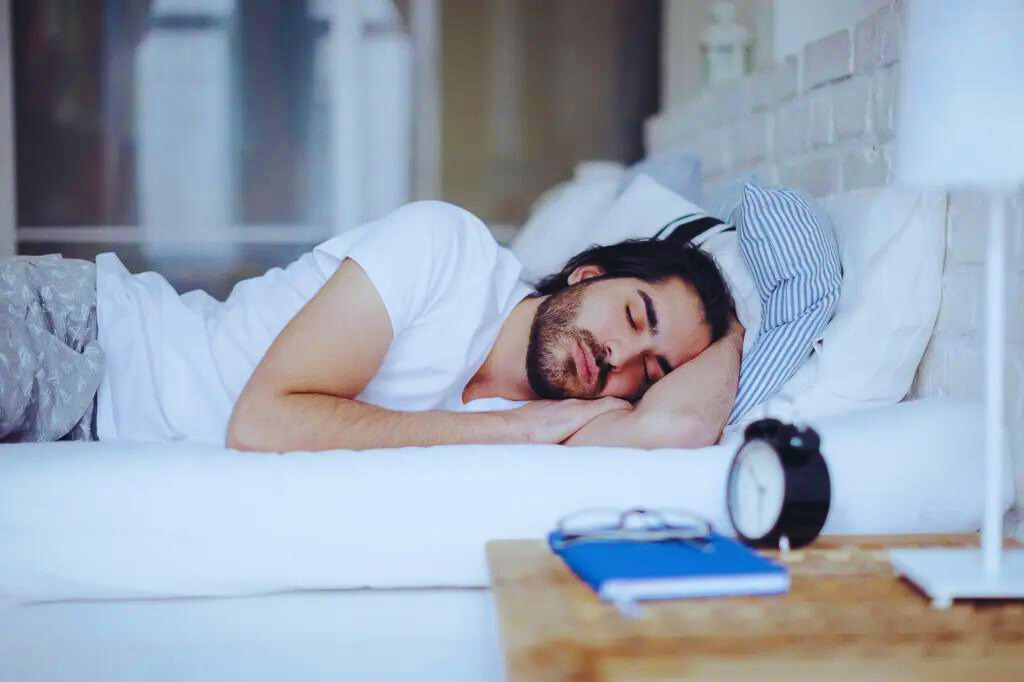

While the clock adjustment is relatively simple, it can affect people’s daily routines. Some individuals might find it challenging to adapt to the shifted time initially, leading to temporary changes in sleep patterns and daily activities. However, the adjustment period is usually brief, and people acclimate to the new schedule within a few days.
In summary, Daylight Saving Time works by shifting the clocks forward in spring to extend evening daylight, promoting energy conservation and maximizing the use of natural light. This practice, though simple in concept, has a significant impact on how people experience daylight during different seasons of the year.
Global Variations of Daylight Saving Time
1. Different Start and End Dates
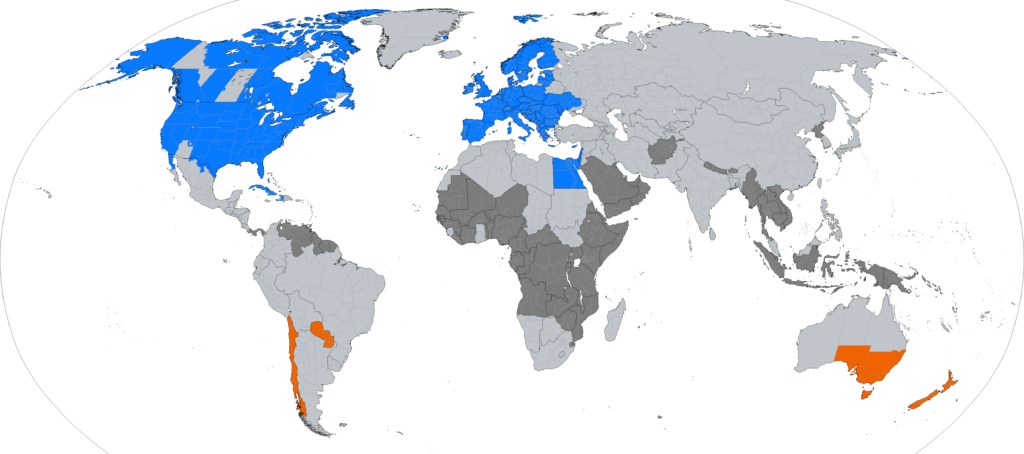
Daylight Saving Time (DST) is observed in various countries around the world, but the start and end dates of this practice can significantly differ. This discrepancy often leads to confusion, especially in our interconnected global society. Here’s an insight into how different countries set their DST schedules:
Factors Influencing Start and End Dates:
- Geographical Location: Countries located at different latitudes experience varying daylight hours throughout the year. Consequently, nations closer to the poles might have more extended periods of daylight in summer, leading them to implement DST for a more significant portion of the year.
- Climate: Countries with extreme climate conditions, such as those with hot summers, might implement DST to ensure that people can make the most out of the cooler evening hours.
- Historical Decisions: Some countries have been following specific DST schedules for decades due to historical decisions made during the adoption of this practice.
Examples of Different Start and End Dates:
United States and Canada:
- Start Date: The second Sunday in March.
- End Date: The first Sunday in November.
European Union:
- Start Date: The last Sunday in March.
- End Date: The last Sunday in October.
Australia:
- Start Date: The first Sunday in October.
- End Date: The first Sunday in April.
Brazil:
- Start Date: The third Sunday in October.
- End Date: The third Sunday in February.
Russia:
- Start Date: Last Sunday in October.
- End Date: Last Sunday in March.
Consequences of Different Schedules:
- Global Business: With businesses operating globally, the misalignment of DST schedules among countries can create challenges in scheduling meetings and international collaborations.
- Travel Arrangements: Travelers need to be aware of DST differences when planning international trips to avoid missing flights or appointments.
- Technological Challenges: Computers, calendars, and other automated systems must be programmed accurately to adjust for the varying DST dates, requiring constant updates and maintenance.
The diversity in start and end dates of Daylight Saving Time across countries highlights the complexity of this practice on a global scale. Understanding these differences is crucial for international communication, travel, and ensuring that technological systems function seamlessly in our interconnected world.
2. Countries that Don’t Follow Daylight Saving Time

While many countries around the world participate in the practice of Daylight Saving Time (DST), there are several nations that choose not to adjust their clocks for various reasons. Here is a list of countries that do not follow DST:
Japan:
Japan doesn’t observe Daylight Saving Time. The country’s consistent sunrise and sunset times throughout the year contribute to this decision.
China:
China does not follow DST. The country’s vast geographical expanse results in relatively consistent daylight hours across regions.
India:
India does not implement Daylight Saving Time. The country’s proximity to the equator ensures relatively consistent day length throughout the year.
Most African Countries:
The majority of African nations do not participate in DST. Consistent daylight hours due to their equatorial location make DST unnecessary.
Arizona and Hawaii (USA):
While most of the United States follows DST, the states of Arizona and Hawaii do not observe the practice. Arizona’s hot climate and Hawaii’s consistent day length are cited as reasons for their non-participation.
Iceland:
Iceland does not observe DST due to its extreme geographical location, resulting in significant variations in daylight hours throughout the year.
Russia:
Although Russia experimented with DST in the past, it was permanently abolished in 2011. The country now operates on standard time throughout the year.
Argentina:
Argentina used to observe DST, but it was discontinued in 2009 due to energy conservation concerns.
Saskatchewan (Canada):
Saskatchewan does not participate in DST, providing consistency for its residents and businesses.
Qatar:
Qatar does not follow DST due to its high temperatures, with daylight saving having minimal impact on energy conservation.
Impact of Non-Participation:
Countries that abstain from DST experience a more consistent daily routine throughout the year. This consistency can simplify scheduling, reduce confusion, and maintain stable working hours for businesses and individuals.
The decision of whether to observe Daylight Saving Time varies based on geographical location, climate, and the preferences of individual nations. While many countries find value in adjusting their clocks seasonally, those that abstain do so to maintain a more stable and predictable daily schedule.
The Impact of Daylight Saving Time on Society
1. Energy Conservation Through Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) is often touted as an energy-saving measure, designed to optimize natural daylight and reduce the need for artificial lighting during the evening hours. The concept behind DST and its impact on energy conservation is a topic of significant interest and debate. Here’s an in-depth look at how DST contributes to energy conservation:
Reduction in Artificial Lighting:

One of the primary goals of DST is to capitalize on extended daylight in the evenings. By moving the clocks forward, people can utilize natural light for longer periods after work or school, reducing their dependence on artificial lighting. This reduction in the use of electric lights directly translates to energy savings, especially in commercial and residential settings.
Decreased Energy Consumption:

Studies have indicated that DST leads to a decrease in overall energy consumption. By minimizing the need for lighting, households and businesses consume less electricity during the evening hours. This reduction in energy demand, even if moderate on an individual scale, has a substantial cumulative effect when extended to entire communities and nations.
Impact on Heating and Cooling:

DST also affects heating and cooling systems. In warmer months, people tend to use air conditioning for shorter durations due to the delayed onset of darkness. In colder months, the effect on heating systems is more nuanced, as mornings are darker, but evenings benefit from extended daylight. However, the net effect is generally positive, leading to reduced energy consumption for both heating and cooling.
Environmental Implications:

The decrease in energy consumption resulting from DST has positive environmental implications. Burning less fossil fuels to generate electricity reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to efforts aimed at combating climate change. Consequently, the environmental benefits of DST extend beyond mere energy conservation, making it a noteworthy practice from a sustainability standpoint.
Economic Impact:

Reduced energy consumption not only benefits households but also positively impacts the economy. Lower energy demands translate to decreased expenditure on electricity, providing economic relief for both consumers and businesses. Additionally, industries reliant on energy-intensive processes experience cost savings, contributing to economic efficiency.
Daylight Saving Time, with its focus on optimizing natural daylight, plays a role in energy conservation by reducing the reliance on artificial lighting and moderating the use of heating and cooling systems. While the energy savings achieved through DST might vary depending on geographic location and individual habits, the overall impact on energy conservation, economic efficiency, and environmental sustainability makes it a practice worth considering.
2. Health and Sleep Patterns During Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) not only affects our daily routines but also has a significant impact on our health and sleep patterns. The biannual clock adjustments can disrupt our internal body clocks, leading to various health issues and changes in sleep behaviors. Here’s a closer look at how DST influences our health and sleep:
Disruption of Circadian Rhythms:
Our bodies operate on a natural internal clock known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates our sleep-wake cycle. The abrupt shift in time during DST can disrupt these rhythms, confusing our body’s internal signals about when to wake up and when to sleep. This disruption can lead to feelings of fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Impact on Sleep Quality:

Studies have shown that the sleep quality of many individuals declines during the transition period of DST. The sudden change in daylight hours can make it challenging to fall asleep at the adjusted time, leading to insufficient sleep duration and poor sleep quality. Sleep disturbances can persist for several days, affecting productivity and overall well-being.
Increased Risk of Health Issues:
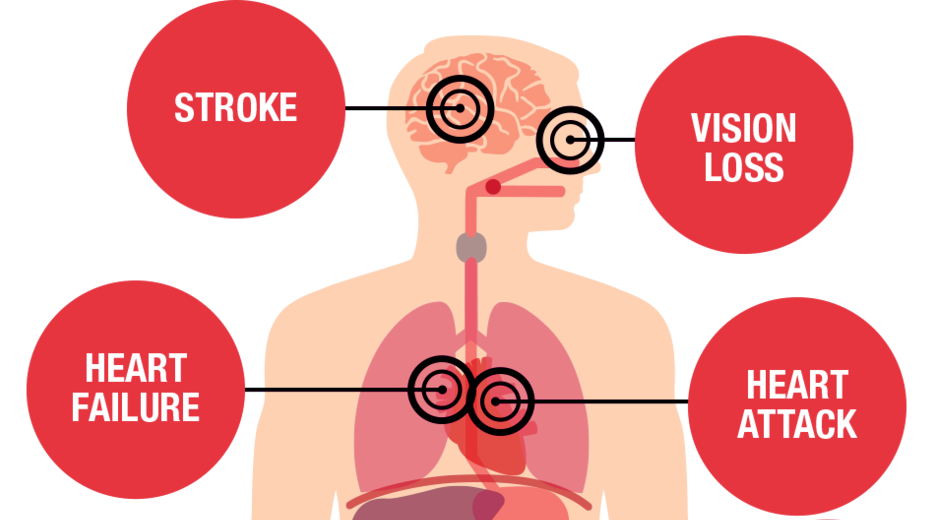
The disruption caused by DST has been linked to an increased risk of various health issues. Research indicates a rise in the number of heart attacks, strokes, and even accidents immediately following the clock changes. The stress and lack of sleep during the adjustment period can strain the cardiovascular system and impair cognitive functions, contributing to these health risks.
Effects on Mental Health:

DST can also impact mental health. The disturbances in sleep patterns can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Lack of proper sleep affects mood regulation, making individuals more prone to experiencing mood swings and feelings of sadness or frustration.
Recommendations for Coping:

To mitigate the negative effects of DST on health and sleep patterns, experts recommend adopting healthy sleep habits and routines, especially during the transition period. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and minimizing exposure to screens before sleep can help improve sleep quality.
Long-term Adjustments:

While our bodies eventually adapt to the new time schedule, the adjustment period can vary from person to person. Some individuals may require more time to acclimate to the changes, emphasizing the importance of being patient with oneself during this period.
The disruption of our circadian rhythms caused by DST can have a significant impact on our health and sleep patterns. Being aware of these effects and taking proactive measures to maintain healthy sleep habits can help minimize the negative consequences, allowing individuals to transition more smoothly through the changing time schedule.
3. Economic Impacts of Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) not only affects our sleep patterns and daily routines but also has notable economic implications. The economic impact of DST is a multifaceted topic, influencing various sectors and aspects of the economy. Here’s an exploration of how DST affects the economy:
Energy Savings:

One of the primary economic benefits of DST is energy savings. By maximizing daylight during the longer days of spring, summer, and early fall, the practice reduces the need for artificial lighting in the evening. This decrease in electricity consumption results in energy cost savings for both households and businesses. According to studies, the energy savings attributed to DST can be substantial, contributing positively to the economy.
Increased Consumer Spending:

Extended daylight hours in the evening encourage people to engage in outdoor activities and shopping after work. This increase in leisure and retail activities can boost consumer spending. Restaurants, entertainment venues, and retail businesses often experience higher sales during the evenings due to the additional daylight, leading to economic growth in these sectors.
Tourism and Hospitality:

The tourism and hospitality industries benefit from DST as well. Longer daylight hours allow tourists to explore attractions, participate in outdoor activities, and dine out later in the evening. Consequently, tourist destinations experience a surge in visitors during the extended daylight period, leading to increased revenue for hotels, restaurants, and local businesses.
Transportation Sector:

The transportation sector, including airlines and public transportation, experiences economic benefits due to DST. Extended daylight in the evening results in increased travel activities. Airlines often schedule more evening flights, accommodating travelers who prefer to fly after work. Public transportation systems also witness higher ridership during the extended daylight hours.
Agriculture and Farming:

While DST primarily affects urban areas, it also has an impact on agriculture. Farmers often adjust their schedules to align with the new daylight hours, allowing for more efficient use of natural light in their operations. This adaptation can lead to improved productivity and reduced energy consumption in farming practices.
Work Productivity:

Studies have suggested that DST can positively influence workplace productivity. With increased daylight in the evening, employees often report improved mood and energy levels. Higher job satisfaction and reduced absenteeism can contribute to enhanced productivity in various industries, positively affecting economic output.
Daylight Saving Time, by maximizing daylight hours in the evening, influences consumer spending, tourism, transportation, and work productivity. Additionally, the energy savings associated with DST have a direct impact on reducing utility costs for individuals and businesses alike. While the economic impacts of DST can vary by region and sector, the overall effect is a dynamic interplay of various factors contributing to economic growth and efficiency.
Daylight Saving Time: Myths vs. Reality
1. Dispelling Common Misconceptions About Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) is a practice that has been met with its fair share of myths and misconceptions over the years. Let’s address and dispel some of the most common misunderstandings associated with DST:
DST Saves Energy:
Misconception: One of the most prevalent beliefs is that DST significantly reduces energy consumption.
Fact: While DST does save energy on lighting, modern studies suggest that the overall energy savings are relatively modest, with the rise in energy use for cooling and electronic devices often offsetting the benefits.
Farmers Benefit from DST:
Misconception: It’s often thought that DST benefits farmers by providing them with more daylight hours to work in the fields.
Fact: Farmers have consistently opposed DST. Cows, for example, don’t adhere to human-set clock changes, making milking schedules difficult to adjust. Farmers base their work on natural daylight, regardless of the clock, so DST adjustments create confusion and disrupt routines.
DST Was Implemented for Farming:
Misconception: Many believe DST was established to assist farmers in their agricultural activities.
Fact: DST was introduced for energy conservation during World War I and later during World War II. It was meant to reduce the need for artificial lighting, especially in industrial and urban areas, and had little to do with farming.
DST Increases Traffic Accidents:
Misconception: There’s a notion that the clock changes during DST lead to an increase in traffic accidents due to disrupted sleep patterns.
Fact: Studies on this topic are inconclusive. While some research suggests a slight uptick in accidents immediately after the clock changes, others argue that people adjust their behavior, negating any significant impact.
DST Is Universally Observed:
Misconception: Many believe that all countries around the world observe DST.
Fact: Numerous countries, especially those near the equator where daylight duration remains consistent throughout the year, do not observe DST. Additionally, some countries that previously practiced DST have discontinued it due to various reasons.
DST Helps Farmers by Providing More Daylight for Crops:
Misconception: Some argue that DST benefits farmers by giving crops more daylight for growth.
Fact: Plants follow natural light cycles, not human-made clock changes. DST does not affect agricultural processes; farmers base their activities on sunlight, not the clock.
Understanding the realities behind Daylight Saving Time is essential in dispelling common misconceptions. While the practice does have certain benefits and impacts, it’s crucial to recognize its limitations and the diverse ways it affects different sectors of society.
By dispelling these myths, we can have a more accurate and informed discussion about the pros and cons of DST, helping individuals and communities make decisions based on facts and actual outcomes.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) is a practice that brings both benefits and drawbacks. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages to gain a comprehensive understanding of this timekeeping phenomenon:
Advantages of DST:
Energy Conservation:
- Advantage: DST reduces the need for artificial lighting in the evenings, leading to energy savings.
- Impact: This reduction in energy consumption, especially in the form of electricity, contributes to environmental conservation and cost savings for both individuals and businesses.
Extended Daylight Hours:
- Advantage: DST provides longer daylight hours in the evenings, allowing for increased outdoor activities, sports, and leisure pursuits after work or school.
- Impact: This extended daylight encourages social interactions, outdoor events, and recreational activities, fostering community engagement and promoting healthier lifestyles.
Boost to Retail and Hospitality Industries:
- Advantage: Longer evenings result in increased consumer spending on shopping, dining, and entertainment.
- Impact: Businesses in the retail and hospitality sectors experience higher sales during the extended daylight hours, stimulating economic growth and creating job opportunities.
Improved Mental Health:
- Advantage: The additional daylight can enhance mood and overall well-being, reducing the prevalence of seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Impact: Individuals often experience improved mental health, increased productivity, and a more positive outlook during the months of DST, especially in regions with limited daylight during winter.
Disadvantages of DST:
Disrupted Sleep Patterns:
- Disadvantage: The abrupt clock changes can disturb sleep patterns, leading to short-term sleep deprivation and fatigue.
- Impact: Disrupted sleep can result in reduced productivity, impaired cognitive function, and an increased risk of accidents, especially during the adjustment period.
Health Issues:
- Disadvantage: DST transitions have been associated with an increase in heart attacks, strokes, and other health problems.
- Impact: The stress associated with the clock changes can strain the cardiovascular system, leading to adverse health effects in susceptible individuals.
Inefficiency and Confusion:
- Disadvantage: The non-uniform adoption of DST across countries and regions can cause confusion, especially in global business and travel.
- Impact: Inconsistent time changes can lead to scheduling challenges, missed appointments, and inefficiencies in international communication and coordination.
Agricultural Challenges:
- Disadvantage: DST can create challenges for farmers, as their schedules are dictated by natural light, not human-made clock changes.
- Impact: Livestock and agricultural activities may be disrupted, potentially affecting productivity and animal well-being, especially during the adjustment period.
Daylight Saving Time presents a complex mix of advantages and disadvantages. While it promotes energy conservation, boosts economic activities, and enhances social interactions, it also brings challenges related to sleep disruption, health issues, inefficiencies, and agricultural practices. Decisions regarding the adoption or discontinuation of DST should consider these factors comprehensively to strike a balance between the benefits and drawbacks for society as a whole.
Embracing the Change
1. Tips for Coping with Daylight Saving Time Changes

The arrival of Daylight Saving Time (DST) often means adjusting our internal clocks to accommodate the shift in time. Coping with this change can be challenging, but there are strategies to help ease the transition. Here are some practical tips to help you cope with DST changes:
Gradual Adjustment:
- Tip: Gradually adjust your sleep schedule in the days leading up to the time change.
- Why: Making small shifts in your bedtime and waking time can help your body adapt more smoothly to the new schedule.
Exposure to Natural Light:
- Tip: Spend time outdoors, especially in the morning, to expose yourself to natural daylight.
- Why: Natural light helps regulate your body’s internal clock, signaling when it’s time to be awake and alert.
Consistent Sleep Routine:
- Tip: Maintain a consistent sleep routine, going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
- Why: Establishing a regular sleep pattern helps your body anticipate when it’s time to rest, improving the quality of your sleep.
Limit Caffeine and Screen Time:
- Tip: Avoid consuming caffeine and minimize screen time, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Why: Caffeine and the blue light emitted by screens can interfere with your ability to fall asleep, making it harder to adjust to the new sleep schedule.
Relaxation Techniques:
- Tip: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga before bedtime.
- Why: Relaxation techniques can help calm your mind and body, making it easier to fall asleep and improve sleep quality.
Maintain a Comfortable Sleep Environment:
- Tip: Keep your bedroom cool, quiet, and dark. Use blackout curtains if necessary.
- Why: A comfortable sleep environment promotes restful sleep, aiding in your body’s adjustment to the new time schedule.
Exercise Regularly:
- Tip: Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid vigorous workouts close to bedtime.
- Why: Exercise promotes overall well-being and can help regulate your sleep patterns, making it easier to adapt to DST changes.
Limit Naps:
- Tip: Avoid long or late-afternoon naps, especially in the days following the time change.
- Why: Excessive napping can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to adjust to the new schedule.
Be Patient and Kind to Yourself:
- Tip: Be patient with your body as it adjusts to the new time schedule.
- Why: It takes time for your internal clock to sync with the external changes. Stress and pressure can further disrupt your sleep.
Seek Professional Help if Needed:
- Tip: If you continue to struggle with sleep after the DST change, consider consulting a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist.
- Why: Persistent sleep disturbances might require professional evaluation and guidance for effective coping strategies.
By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can minimize the challenges associated with Daylight Saving Time changes, ensuring a smoother transition and better sleep quality.
2. Celebrating the Extra Hour of Daylight During Daylight Saving Time

Daylight Saving Time (DST) offers an extra hour of daylight in the evenings, creating a unique opportunity to make the most out of these extended hours. Here are creative and enjoyable ways to celebrate the additional daylight during DST:
Outdoor Activities:
- Idea: Organize outdoor picnics, barbecues, or family gatherings in parks or gardens.
- Why: Enjoy the pleasant weather and longer evenings with loved ones, creating memorable moments in the great outdoors.
Gardening and Green Spaces:
- Idea: Spend time tending to your garden or visit local botanical gardens and parks.
- Why: The extra daylight is perfect for nurturing plants, cultivating beautiful gardens, and appreciating the natural beauty of green spaces.
Sports and Exercise:
- Idea: Engage in sports activities like cycling, hiking, or evening jogs.
- Why: Take advantage of the extra daylight to stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle, all while enjoying the beauty of the outdoors.
Arts and Crafts:
- Idea: Set up an outdoor art station for painting, drawing, or crafting.
- Why: Natural daylight enhances creativity. Create art inspired by the changing light, capturing the essence of the golden hour.
Evening Strolls:
- Idea: Take leisurely evening strolls in your neighborhood or along scenic routes.
- Why: Witness the transformation of the surroundings as the sun sets, and enjoy the calming atmosphere during these peaceful walks.
Al Fresco Dining:
- Idea: Dine outdoors at restaurants or set up a cozy dinner on your patio.
- Why: Enjoy delicious meals with friends or family in the open air, savoring the culinary delights under the twilight sky.
Photography Sessions:
- Idea: Explore photography during the golden hour and capture the beauty of dusk and sunset.
- Why: The soft, warm light during the extra hour of daylight provides excellent opportunities for stunning photographs.
Community Events:
- Idea: Attend local community events, concerts, or outdoor theater performances.
- Why: Many communities host special events during DST, allowing you to socialize, enjoy entertainment, and connect with neighbors.
Star Gazing:
- Idea: Set up a telescope or simply lie on a blanket and observe the night sky.
- Why: With longer evenings, you have more time to appreciate the wonders of the night, including stars, constellations, and celestial events.
Family Bonding:
- Idea: Plan family game nights, storytelling sessions, or stargazing adventures together.
- Why: Utilize the extra daylight to strengthen family bonds, create cherished memories, and enjoy quality time with your loved ones.
Embrace the additional hour of daylight during DST by indulging in these delightful activities. Whether you prefer outdoor adventures, artistic pursuits, or simply spending quality time with family and friends, the extended evening hours offer endless possibilities for enjoyment and relaxation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the biannual ritual of changing the clocks forward and backward is a testament to humanity’s adaptability and our effort to harmonize our lives with the natural rhythms of the Earth. Understanding the significance behind these time shifts can help us embrace the change with a positive mindset and make the most out of the altered hours of daylight.
Read also: Why Was Kezia Afraid of Her Father?
Daylight saving time was introduced to make better use of daylight during the longer days of spring, summer, and early fall, ultimately conserving energy.
Countries near the equator, such as Ecuador and Indonesia, and some regions like Saskatchewan in Canada, do not observe daylight saving time.
Yes, the sudden time change can disrupt sleep patterns and circadian rhythms, leading to temporary health issues like fatigue and irritability.
Critics argue that daylight saving time disrupts sleep, and productivity, and can lead to health problems, outweighing its energy-saving benefits.
To prepare for the time change, gradually adjust your sleep schedule, expose yourself to natural sunlight in the morning, and maintain a consistent bedtime routine.