Introduction to Global Warming
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by burning fossil fuels. It occurs when carbon dioxide (CO2) and other air pollutants accumulate in the atmosphere, trapping sunlight and solar radiation, which would normally escape into space. This phenomenon has led to the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century. Contributing to climate change, global warming affects weather, oceans, ecosystems, and more, as it results from the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Climate change itself represents a long-term change in the average weather patterns that define Earth’s local, regional, and global climates. The increase in average world temperatures due to the greenhouse effect, where certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat, is a key aspect of global warming.
The Basics: A Warmer Earth
The effects of a warmer Earth are manifold and profound. They include melting polar ice caps and mountain glaciers, contributing to rising sea levels, and altering habitats for flora and fauna. Climate change driven by global warming also manifests in more extreme weather patterns, such as increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, and heat waves. Human activities, especially emissions of greenhouse gases, are identified as the unequivocal cause of global warming, leading to a continuous rise in global surface temperatures. This warming poses a serious threat to life on Earth, including widespread flooding and the potential for extreme weather events.
Causes: Not Just Your Car’s Exhaust

While vehicle exhaust is a well-known source of air pollution, contributing to harmful substances like benzene and acetaldehyde, the causes of air pollution extend beyond transportation. Industries emit smoke and pollutants that significantly impact air quality. Household air pollution, particularly from the inefficient combustion of solid fuels (wood, coal, charcoal, crop waste, dung) and kerosene, is a leading cause of degraded indoor air quality. Furthermore, natural processes such as wildfires and the decomposition of organic matter in soils also contribute to air pollution levels.
The Science Behind It
Greenhouse Gases: The Invisible Blanket
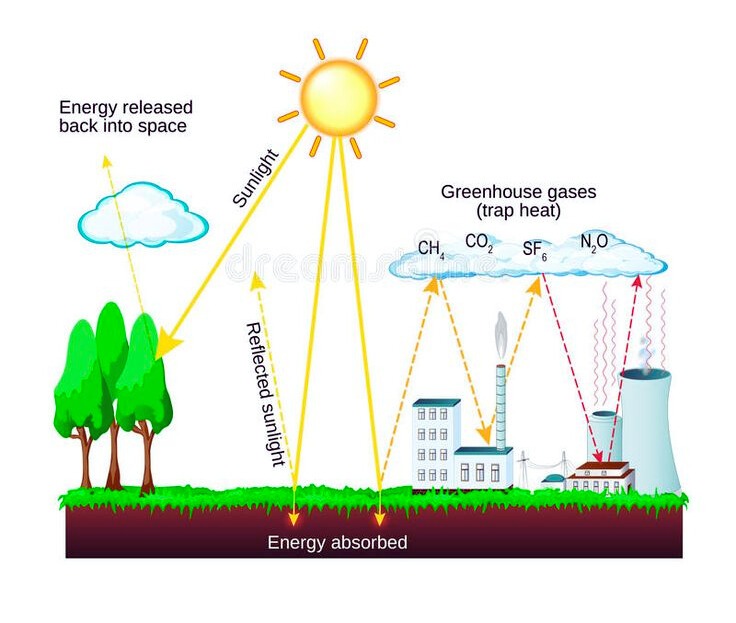
Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor, function as an invisible blanket around Earth. They trap heat in the atmosphere through a natural process known as the greenhouse effect. This process involves the absorption of infrared radiation (light) by greenhouse gas molecules, preventing some of the heat from escaping back into space. As these gases absorb and emit infrared radiation, they warm the Earth’s surface and the lower atmosphere, thus maintaining the planet’s temperature at a level necessary for life as we know it. While this effect is essential for sustaining Earth’s habitable climate, human activities have intensified the effect by increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change.
The Sun’s Role: It’s Not All About Heat
The Sun influences Earth beyond just providing heat and light. Its impact extends to various environmental and atmospheric processes:
- Climate Regulation: The Sun’s energy is essential for the Earth’s climate system, affecting weather patterns, atmospheric circulation, and ocean currents. The absorption and reflection of sunlight by the Earth’s surface and atmosphere are crucial in maintaining the planet’s temperature.
- Nonthermal Radiation: Beyond visible light and heat, the Sun also emits nonthermal radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) rays, which have significant effects on the Earth’s atmosphere and biological life, influencing everything from weather phenomena to the health of living organisms.
- Ecosystems and Photosynthesis: Sunlight drives photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce oxygen and energy, forming the base of most Earth’s ecosystems. This process not only supports life by providing oxygen but also sequesters carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
- Aerosols Interaction: The interaction between sunlight and aerosols in the atmosphere can affect the climate. Aerosols can scatter and absorb sunlight, influencing Earth’s energy balance and, consequently, its climate.
Thus, the Sun’s role encompasses a wide range of effects that are fundamental to sustaining life on Earth and maintaining its climate.
Effects and Consequences
Melting Ice Caps: More Water Than Land?

The melting of ice caps is a critical concern due to its significant impacts on global sea levels and ecosystems:
- Rising Sea Levels: The primary consequence of melting glaciers and ice caps is the rise in global sea levels. Land ice, such as glaciers, adds water to the world’s oceans when it melts, directly contributing to sea level rise. This process is distinct from the melting of sea ice, which doesn’t contribute to sea level rise as it’s already in the water.
- Coastal Erosion and Flooding: As sea levels rise, coastal areas are more susceptible to erosion and flooding. This can lead to the displacement of communities, loss of habitat for wildlife, and destruction of ecosystems.
- Climate Feedback Loops: The loss of ice, particularly in the Arctic, reduces the Earth’s albedo effect, meaning less sunlight is reflected back into space, leading to further warming and ice melt in a self-reinforcing cycle.
While the total submersion of land under water due to melting ice caps is an extreme scenario, the consequences outlined above are severe and warrant significant concern and action to mitigate climate change and its effects on ice melt.
Weather Gone Wild: The New Normal
The increasing prevalence of extreme weather events represents a significant shift in our planet’s climate system, often referred to as the “new normal.” This change is largely attributed to human-induced climate change, which has altered weather patterns and increased the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Here are some of the key effects and consequences:
- Increased Heatwaves: Global warming has led to more frequent and severe heatwaves, impacting human health, agriculture, and natural ecosystems. Heat stress can cause heatstroke and exacerbate conditions such as heart disease.
- More Intense Storms and Hurricanes: Warmer ocean temperatures fuel more powerful storms and hurricanes, leading to catastrophic damage to infrastructure, loss of life, and economic disruptions.
- Heightened Flooding Risks: The combination of sea-level rise, intense rainfall events, and storms has increased the risk of flooding in coastal and low-lying areas, endangering communities and leading to significant economic losses.
- Severe Droughts: Climate change also contributes to more prolonged and severe droughts, affecting water supply, agriculture, and food security. Drought conditions can lead to wildfires, loss of crops, and water scarcity.
- Displacement and Health Risks: Extreme weather events can displace populations and increase risks to human health, including injuries, waterborne diseases, and mental health issues due to trauma and displacement.
- Ecosystem and Biodiversity Loss: Extreme weather can devastate ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity. Species that cannot adapt or migrate face increased risks of extinction.
Addressing the root causes of climate change and enhancing our resilience to its impacts are critical steps in mitigating these effects and safeguarding our planet for future generations.
Mitigation and Adaptation
Renewable Energy: Sun, Wind, and Water

Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydro, play a pivotal role in climate change mitigation and adaptation. They emit little to no greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels, making them integral in reducing the global carbon footprint and combatting climate change. Here’s how they contribute:
- Solar Energy: Harnessing sunlight to produce electricity or heat reduces reliance on coal and gas. Solar power is readily available and increasingly cost-effective, contributing significantly to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity, offering a clean, efficient, and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Wind energy is a key player in reducing global carbon emissions and can be deployed both onshore and offshore.
- Hydropower: Water energy, generated through the movement of water in rivers and oceans, provides a stable and low-carbon source of electricity. It supports climate adaptation by offering a reliable energy source even in changing climate conditions.
Renewable energy not only mitigates climate change by lowering emissions but also enhances the resilience of communities against climate impacts through decentralized and diversified energy sources.
Lifestyle Changes: Every Bit Helps
Individual actions can have a significant impact on climate change mitigation and adaptation. Here are key lifestyle changes that can help:
- Reduce Meat Consumption: Eating more vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, and reducing meat intake can save resources like water and land, and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
- Minimize Car Use: Opt for walking, cycling, or public transport to reduce your carbon footprint. Car-sharing and choosing electric vehicles also contribute to less pollution.
- Energy Efficiency: Improve home energy efficiency by using LED lighting, energy-saving appliances, and ensuring proper insulation to reduce energy consumption.
- Support Renewable Energy: Invest in renewable energy sources for your home, such as solar panels, to decrease reliance on fossil fuels.
- Eco-friendly Purchases: Choose products with minimal packaging, opt for sustainable brands, and reduce waste by recycling and composting.
Every small action counts towards a larger impact on mitigating climate change and adapting to its effects.
The Role of Policy and Legislation
Global Agreements: Working Together for the Planet
International environmental agreements and treaties play a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to tackle environmental challenges. In 2024, key agreements continue to focus on various sustainability objectives, emphasizing the importance of global cooperation in addressing climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss. The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), for instance, underscores the growing importance of such multilateral cooperation, particularly in improving air quality and countering the triple planetary crisis through legal frameworks and policy initiatives. The Paris Agreement stands as a notable success, mandating countries to set emissions-reduction targets, and highlighting the significance of policy and legislation in achieving environmental goals. These agreements facilitate collective action, ensuring that trade and economic growth considerations are balanced with the urgent need for environmental preservation and climate action.
Local Initiatives: Small Steps, Big Impact
Local initiatives play a pivotal role in climate change mitigation and adaptation, showcasing how community actions and policies at the municipal level can contribute significantly to the global fight against climate change. Despite adaptation often being considered secondary to mitigation in policy agendas, local governments worldwide are recognized for their essential role in implementing urgent climate change policies. Community actions, integrated with effective policies, are key to addressing climate change challenges. Municipal policies, in particular, have been highlighted for their potential to significantly contribute to climate mitigation, shaping local climate governance. Furthermore, smart growth policies are seen as instrumental in both mitigating and adapting to climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and making communities more resilient.
What Can You Do?
At Home
Taking action against climate change starts at home. Here are some practical steps you can take:
- Monitor Your Thermostat: Adjusting your heating and cooling can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
- Improve Energy Efficiency: Insulate walls and attics to reduce energy consumption.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Embrace these principles in daily life to minimize waste.
- Adopt Eco-friendly Transportation: Opt for walking, cycling, or electric vehicles when possible.
- Install a Heat Pump: Switching to a heat pump can reduce your home’s greenhouse gas emissions.
- Support Sustainable Brands: Purchase products from companies that prioritize sustainability.
Every small action contributes to a larger impact in the fight against climate change.
In Your Community
Engaging in your community to support environmental and climate justice involves several strategic actions:
- Advocate for Meaningful Participation: Ensure that community voices are heard in environmental decision-making processes, particularly during Superfund cleanups.
- Participate in Federal Facility Cleanups: Get involved in community discussions about cleanups at federal facilities to ensure they meet local needs.
- Support Environmental Justice Policies: Advocate for and support policies aimed at revitalizing the nation’s commitment to environmental justice, ensuring all communities benefit equally.
- Leverage Funding Opportunities: Engage with programs like the EPA’s $2 billion Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants to support local environmental justice initiatives.
- Demand Inclusive Decision-Making: Call for federal agencies to include community input in environmental decision-making, ensuring those most affected have a say.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The urgent need for exponential climate action is clear. As we step into 2024, several key strategies emerge from global discourse:
- Implement the IEA Net Zero Pathway: A foundational step to drastically reduce emissions and phase out fossil fuels to limit global warming.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Developing strategies to adapt to changing climates and enhance resilience is critical for communities worldwide.
- Motivate Behavioral Change: Research highlights the importance of motivating individuals and communities to change behaviors that negatively impact the climate.
- Set Clear Goals: Establishing core goals, as seen in the 2024 Climate Action Plan, provides a structured approach to achieving significant progress.
- Invest in Clean Energy: Prioritizing investments in adaptation, resilience, and clean energy can help avoid conflicts and increase food security and prosperity.
- Individual Contributions: Encouraging actions like reducing energy consumption, promoting sustainable mobility, and supporting sustainable agriculture are vital.
Read also: What Is Considered a Fever?
FAQs
Q. What is the current projection for global temperature rise?
The worst projection for 2024 is that the chance for the average global temperature to rise above 1.5°C has increased to almost 50%.
Q. How has climate change affected weather patterns in 2024?
In 2024, storms, wildfires, and other threats are expected to be exacerbated by climate change, continuing the trend of increasing climate crises.
Q. What records have been broken by the global climate in 2024?
February 2024 saw the warmest December–February period in the 175-year record, 1.36°C (2.45°F) above the 20th-century average. January 2024 was also the warmest January on record globally, with an average ERA5 surface air temperature of 13.14°C, 0.70°C above the 1991-2020 average.
Q. What are the chances of 2024 being the warmest year on record?
There is a 22% chance that 2024 will rank as the warmest year on record and a 99% chance it will be among the top ten warmest years.




