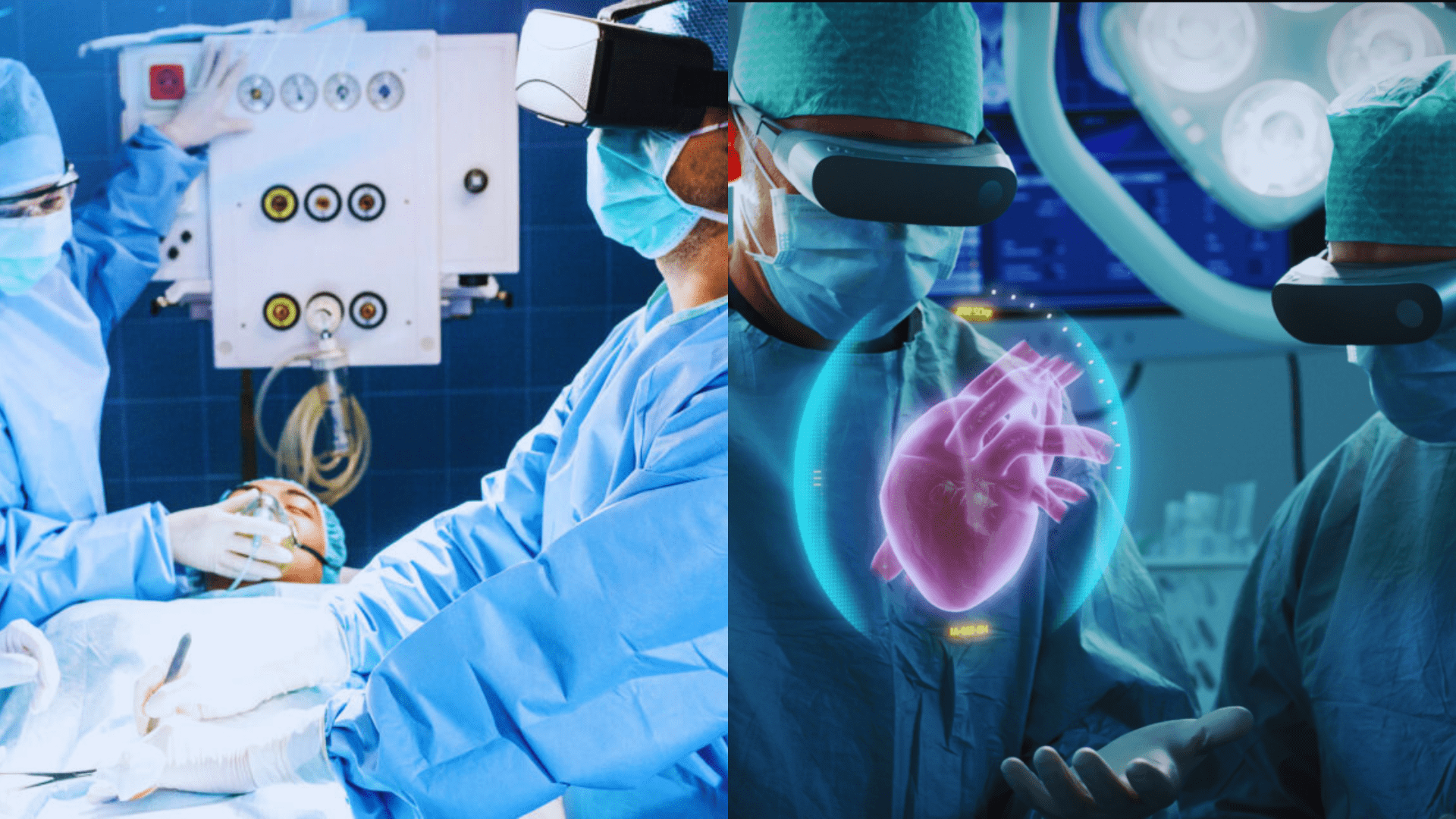
Introduction to Extended Reality in Surgery
Extended Reality (XR) in healthcare, particularly in surgery, encompasses a range of technologies from fully immersive virtual environments to augmented real-world settings. These innovations offer significant potential to enhance surgical outcomes by improving precision, facilitating better pre-operative planning, and offering comprehensive training tools. XR technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), allow surgeons to visualize complex anatomical structures in 3D, overlaying digital information onto the physical world during procedures. This capability can lead to more accurate diagnoses, precise surgical interventions, and improved patient safety. The application of XR in surgical science is gaining momentum, with ongoing research and development aimed at integrating these technologies further into medical practice to support surgeons’ vision, imaging, and localization needs.
Defining Extended Reality (XR)

Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and any future immersive technologies. XR represents a broad category of technologies that alter reality by either overlaying digital information onto the real world (AR), creating a completely virtual experience (VR), or blending both real and virtual elements (MR). Introduced in 1991, XR has evolved to include a spectrum of applications that aim to create more immersive digital experiences. By integrating digital content with the physical world, XR technologies have the potential to transform numerous industries, including education, healthcare, entertainment, and manufacturing, by providing more engaging and interactive user experiences.
The Evolution of Surgical Techniques
The evolution of surgical techniques spans from ancient times to the present, highlighting a journey of continuous adaptation and innovation. Initially, surgery was rudimentary, largely limited by the lack of knowledge and technology. Over the centuries, advancements in surgical methods have been closely tied to technological progress and a deeper understanding of human anatomy and physiology. The last 20 years have seen a significant shift, with technology radically changing surgical care. This era is marked by the introduction and rapid expansion of minimally invasive techniques, enhanced by digital imaging, robotics, and virtual reality, leading to increased precision, reduced patient recovery times, and lower risk of complications. The historical perspective on surgical innovation reveals a field that has evolved from simple manual procedures to complex, technology-driven interventions, promising even greater advancements in the future.
Key Benefits of XR in Surgical Science

Extended Reality (XR) introduces several transformative benefits to surgical science, notably:
- Enhanced Surgical Training and Education: XR provides immersive, realistic simulations for surgical training, allowing for hands-on practice without patient risk.
- Improved Preoperative Planning: Utilizing XR for preoperative planning enables more precise surgical strategies, potentially leading to better outcomes and shorter operation times.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: By improving all phases of the surgical process, XR offers the chance to deliver a better overall patient experience.
- Advancements in Robotic Surgery: Incorporating XR into surgical procedures improves the capabilities of robotic surgery, making surgeries less invasive and more accurate.
- Benefits in Preoperative Planning and Neuronavigation: Especially in complex fields like neurosurgery, XR technologies have shown significant benefits for tumor surgery planning and execution.
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
Extended Reality (XR) technologies significantly enhance precision and accuracy in surgical science. The integration of XR, encompassing both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), offers a revolutionary approach to surgical procedures and planning. Key benefits include:
- Improved Surgical Planning: XR allows for interactive and accurate 3D visualizations of the patient’s anatomy, facilitating more precise surgical planning and execution.
- Enhanced Surgical Precision: Studies highlight XR’s role in elevating surgical precision and patient safety, underscoring its potential to minimize errors and improve outcomes.
- Augmented Surgeries: XR technologies provide real-time data overlay during procedures, enabling surgeons to perform with greater accuracy and confidence.
- Innovative Technologies: Developments like the DigiLoupes technology demonstrate XR’s capability to enhance complex surgeries such as spine surgery through ergonomic and 3D visual support systems.
- Anticipated Advancements: The ongoing development of virtual surgery systems promises even higher levels of realism and precision, setting new standards for surgical procedures.
Real-time Data Overlay
Real-time data overlay, facilitated by Extended Reality (XR) technologies, represents a transformative advancement in surgical science. This innovation allows surgeons to access and interact with real-time data and visual aids directly within their field of view during procedures. Key applications and benefits include:
- Enhanced Surgical Precision: By overlaying detailed, reconstructed models of a patient’s anatomy onto the surgical field, surgeons can perform procedures with greater accuracy and confidence.
- Complex Procedure Facilitation: XR technologies enable the performance of more complex surgeries by providing surgeons with real-time data and visual guidance, which can be crucial for navigating intricate anatomical structures.
- Improved Surgical Planning: Utilizing preoperative images, data, and XR technologies, surgeons can better plan their surgical approach, improving the overall safety and effectiveness of the procedure.
- Educational Value: XR’s real-time data overlay capabilities are also being explored for their potential in surgical education, providing residents with increased exposure to surgical procedures in a controlled, virtual environment.
3D Visualization
3D visualization in surgery, particularly in vitreoretinal procedures, represents a significant leap forward in medical technology. This advancement offers surgeons enhanced depth perception, clarity, and resolution during operations. By employing digital microscopes and 3D visualization systems, surgeons gain a comprehensive view of the surgical field, which is pivotal for intricate procedures. These technologies not only improve surgical outcomes but also minimize risks associated with surgeries by providing a more immersive and detailed view of the patient’s anatomy. The integration of augmented reality with 3D visualization further enhances these benefits, offering a futuristic approach to surgical procedures by overlaying critical information directly onto the surgeon’s field of view.
Improved Training and Education
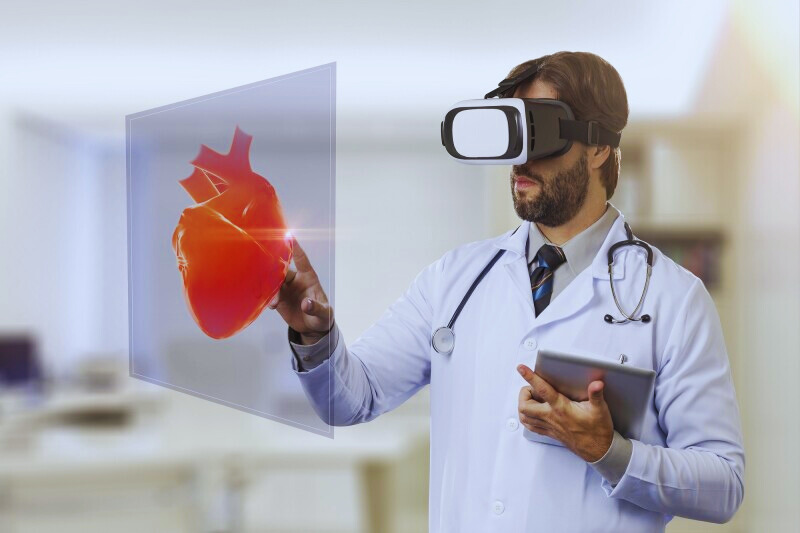

The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) and Extended Reality (XR) into medical training has significantly advanced how healthcare professionals are educated. These technologies offer a risk-free, cost-effective method for honing surgical skills, allowing for repeatable, immersive surgical simulations. They are employed in medical schools and healthcare institutions to enhance learning experiences, providing realistic training environments for complex anatomy lessons and surgical procedures. XR’s application in surgery simulation is particularly promising, offering immersive training experiences that are both hyper-realistic and safe. This technology is pivotal in areas such as surgical training, pre-operative preparation, and intra-operative guidance, contributing to improved surgical outcomes and patient care.
Virtual Reality Simulations
Virtual Reality (VR) simulations are revolutionizing surgical training, offering a risk-free, cost-effective method to enhance skills and improve performance significantly. Research from UCLA highlighted a remarkable 130% improvement in surgical resident training using VR, with tactile haptic feedback showing promising results. VR surgery training advancements allow medical education to evolve, providing immersive, realistic experiences that are safe for learners. The medical simulation industry expects significant trends in 2024, focusing on increasing realism and efficacy through VR. A study published by Osso VR indicates that VR training in orthopedic surgical education outperforms traditional methods, confirming its effectiveness. As VR systems continue to advance, they are becoming an integral addition to surgical education, necessitating an evaluation of their potential benefits and limitations. The most recent innovations in VR for surgical education are systematically reviewed to explore their impact and future potential.
Augmented Reality in Live Surgeries
Augmented Reality (AR) has been making significant strides in the field of surgery, offering innovative ways to enhance surgical precision and efficiency. AR technology integrates digital information with the physical environment, providing surgeons with real-time, interactive visualizations of anatomical structures during procedures. This technology has been applied across various surgical fields, with promising results in improving outcomes and training. For instance, Johns Hopkins performed its first AR surgeries on patients, demonstrating the practical application and benefits of AR in live surgical settings. Studies and clinical trials, such as those cited by Dennler et al. 2021, confirm the growing acceptance and feasibility of AR in operating rooms, highlighting its potential to transform surgical practices by allowing more accurate visualization and control during procedures. As AR technology continues to evolve, it is expected to enhance surgical training and execution further, making surgeries safer and more efficient.
Increased Patient Safety
Extended Reality (XR) technology significantly enhances patient safety in surgical procedures. XR, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), offers surgeons advanced visualization tools that lead to better planning and execution of surgeries. This technology minimizes the risk of accidental surgical trauma by allowing precise navigation and manipulation of surgical instruments within the patient’s body. Additionally, XR-assisted surgery improves the surgeon’s ability to visualize anatomical details, directly contributing to enhanced patient safety during operations. XR technology ensures a safer, more efficient surgical process by improving every phase of the patient experience, from diagnosis to treatment. Moreover, the integration of XR in surgical education and training enables medical professionals to gain comprehensive exposure and hands-on experience in a risk-free virtual environment, further safeguarding patient well-being during actual surgeries.
Preoperative Planning
Extended Reality (XR) significantly enhances preoperative planning, offering surgeons unprecedented spatial awareness and visualization of anatomical structures. This improvement in planning is crucial for complex surgeries, where understanding the specific details of a patient’s anatomy can greatly influence the outcome. XR technologies, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), allow for a detailed preoperative analysis by creating immersive, interactive models of patient anatomy. These models can be manipulated and observed from various angles, providing a comprehensive understanding of the surgical field before the actual procedure begins. Such preparation is instrumental in reducing surgical errors, optimizing procedural strategies, and ultimately enhancing patient safety and outcomes.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive surgery is expected to see a significant rise in popularity in 2024, driven by advancements in surgical techniques and technologies. These procedures, which include laparoscopic, robotic, and other less invasive techniques, offer numerous benefits over traditional open surgery, such as reduced pain, quicker recovery times, and lower risks of complications. The future of these procedures looks promising, with innovations in minimally invasive innovations and techniques being continuously developed and refined. These advancements are not only limited to general and colorectal surgery but extend across various medical fields, including cosmetic surgery where techniques like minimally invasive arm lifts are being explored. The growing demand for these surgeries is a testament to their effectiveness and the ongoing progress in medical technology and surgical methods.
Better Patient Outcomes

The integration of Extended Reality (XR) technologies in healthcare has shown promising potential for enhancing patient outcomes. XR, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), offers innovative approaches for patient education, medical training, and therapeutic interventions. Studies and expert analyses suggest that XR can significantly improve learning outcomes for healthcare professionals, leading to better patient care. Additionally, XR applications in pain management, physical therapy, and behavioral health assessment have demonstrated benefits such as reduced pain perception, accelerated recovery times, and improved ability to triage effectively. The use of XR can also lower the physical impact on patients, shorten recovery times, and enhance the quality of care. Collectively, these advancements underscore the immense potential of XR technologies in revolutionizing healthcare delivery and patient experiences.
Reduced Recovery Times
The application of Extended Reality (XR) technologies in surgical science significantly contributes to reduced recovery times for patients. XR, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), enhances surgical procedures through improved visualization, precision, and patient education. Studies indicate that XR can minimize postoperative complications by offering surgeons better planning and navigational tools during operations. Additionally, VR has been shown to aid in pain reduction during rehabilitation, fostering a quicker and more confident recovery process. These technologies also support postoperative care by supplementing recovery treatments, further contributing to shortened recovery times. Overall, the integration of XR into surgical practices not only enhances the efficiency and safety of surgical procedures but also significantly accelerates patient recovery, leading to better health outcomes.
Lower Risk of Complications
Augmented Reality (AR) in surgery significantly lowers the risk of complications by enhancing the precision and safety of surgical procedures. AR technology provides surgeons with real-time, three-dimensional images of the patient’s anatomy during surgery, improving their ability to see hidden organs and accurately target surgical sites. This improved visualization reduces the likelihood of errors, minimizes the risk of damaging adjacent tissues, and ensures more accurate resections, thereby decreasing the chance of relapse and postoperative complications. Furthermore, the precision offered by AR contributes to fewer patient problems and infections post-surgery, promoting a quicker and safer recovery. Overall, the integration of AR into surgical practices represents a significant advancement in reducing procedure-related complications and enhancing patient outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
In the context of 3D modeling and visualization, several key challenges and considerations emerge:
- Complexity: Handling complex shapes or intricate details can be daunting. It’s advisable to break down the model into simpler parts to manage this complexity effectively.
- Data Quality: The quality of underlying data is crucial. Flawed, incomplete, or biased data can significantly limit the effectiveness and accuracy of 3D visualizations.
- Technology Integration: Incorporating AR and VR technologies in fields like medical education requires careful consideration of the technology’s capabilities and limitations to ensure it enhances learning and training outcomes.
- User Experience: In VR applications, achieving an immersive user experience is essential. This involves considerations around pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to create a convincing virtual world.
Technological Limitations
Technological advancements in healthcare, while offering numerous benefits, come with their set of limitations:
- Connectivity and Access: While technology enables better connectivity between healthcare professionals and patients, there’s an implicit need for reliable internet access, which may not be universally available, thus limiting its reach and effectiveness.
- Implementation Challenges: The enthusiasm for medical technologies often meets hurdles during implementation, such as high costs, training needs, and adapting to new workflows. These challenges can delay or limit the adoption of potentially beneficial technologies.
- Surgical Risks: Even minimally invasive surgery, which is designed to reduce risks and recovery time compared to open surgery, carries inherent risks. These can include complications related to small incisions and the precision required in such procedures.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The implementation of VR and AR in healthcare raises several ethical and privacy concerns:
- Privacy and Data Security: Ensuring patient information is protected and securely handled is paramount. Healthcare providers and technology developers must prioritize safeguarding personal data against unauthorized access or breaches.
- Informed Consent: Clear guidelines are necessary for obtaining informed consent from patients, ensuring they understand how VR/AR technologies will be used in their care and the potential risks involved.
- Mental and Social Side Effects: There’s a need to address the mental and social impacts of prolonged VR/AR use, such as unrealistic expectations, potential addiction, or altered perception of reality.
- Anonymity and Facial Recognition: The use of AR technologies that incorporate facial-recognition must balance the benefits with the right to anonymity, addressing concerns over surveillance and privacy intrusions.
The Future of XR in Surgery
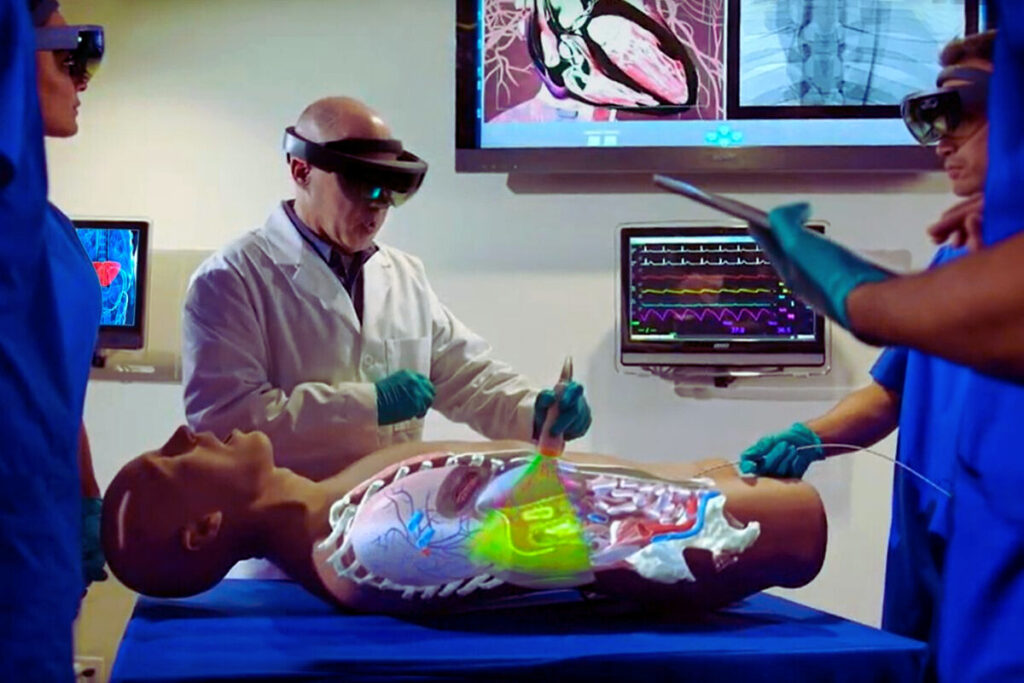
Extended Reality (XR) is set to revolutionize surgical science by merging virtual and augmented reality to enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes. XR applications in surgery can facilitate the detection of complex medical conditions such as arthritis, tissue degeneration, tumors, and fractures. Moreover, it provides invaluable pre-surgical planning and simulation opportunities, allowing surgeons to rehearse procedures in a risk-free environment. The market for XR in healthcare is expected to grow significantly, with projections reaching USD 463.7 billion by 2026. This growth is attributed to its wide range of applications, including surgical training, planning, rehabilitation, and physical therapy. XR’s benefits extend to surgical training, offering a promising future for enhancing the skills and knowledge of medical professionals through immersive, hands-on experiences.
Ongoing Developments and Potential
The landscape of technology, especially in healthcare and augmented reality (AR), is poised for significant growth and transformation in 2024. The integration of Extended Reality (XR) technologies in healthcare is revolutionizing surgical simulations and training for medical professionals, indicating a broader adoption of immersive technologies for practical and educational purposes. The healthcare sector, in particular, is set to experience groundbreaking advancements amidst unique challenges, with technology playing a pivotal role in shaping the journey forward. Spatial computing, including advancements in hardware and wearables, is identified as a critical area of growth, suggesting an increase in the integration of AR and Virtual Reality (VR) into daily life and professional environments. Additionally, the report on medical device trends highlights the ongoing innovations and their implications for businesses, underscoring the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements. These developments signal a future where technology, particularly AR and XR, will play a crucial role in enhancing human capabilities and transforming healthcare delivery.
The Role of AI in Enhancing XR Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) significantly enhances Extended Reality (XR) applications in surgery, offering innovative ways to improve surgical training, pre-operative planning, and execution. AI’s role includes evaluating performance and providing personalized feedback in surgical simulators, thereby enhancing the learning experience for medical professionals. Furthermore, XR technologies, augmented by AI, offer substantial benefits in surgical science, particularly in pre-operative planning. Studies have demonstrated that Virtual Reality (VR), a subset of XR, can improve surgeons’ spatial understanding, crucial for complex surgical procedures. Additionally, the integration of XR and AI in medicine opens up revolutionary possibilities, potentially transforming fields beyond surgery, including education and the execution of medical procedures, with future applications heavily reliant on the advancement of AI technology.
Conclusion
The integration of extended reality into surgical science is not just a technological leap; it’s a paradigm shift that promises to redefine what’s possible in medicine. From transforming training and education to enhancing precision and patient outcomes, the benefits are profound. Yet, as we navigate this new frontier, we must also address the technological, ethical, and privacy challenges that come with it.
Read also: What Would Be an Ideal Scenario for Using Edge Computing Solutions?
FAQs
Q. What is extended reality (XR)?
Extended reality (XR) is a collective term for virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies that blend the virtual and real worlds or create an immersive digital environment.
Q. How does XR improve surgical precision?
XR technologies like AR can overlay digital images, such as CT scans, onto the physical world, helping surgeons perform procedures with greater accuracy and confidence.
Q. Can XR in surgery lead to better patient outcomes?
Yes, by enabling minimally invasive procedures and allowing for detailed preoperative planning, XR can reduce recovery times and lower the risk of complications.
Q. What are the challenges of integrating XR in surgical science?
Challenges include technological limitations, such as hardware and software issues, as well as ethical and privacy concerns related to the use of digital data in healthcare.
Q. What does the future hold for XR in surgery?
The future of XR in surgery is promising, with ongoing developments in technology and the potential for AI to enhance XR applications, leading to more personalized and precise surgical interventions.