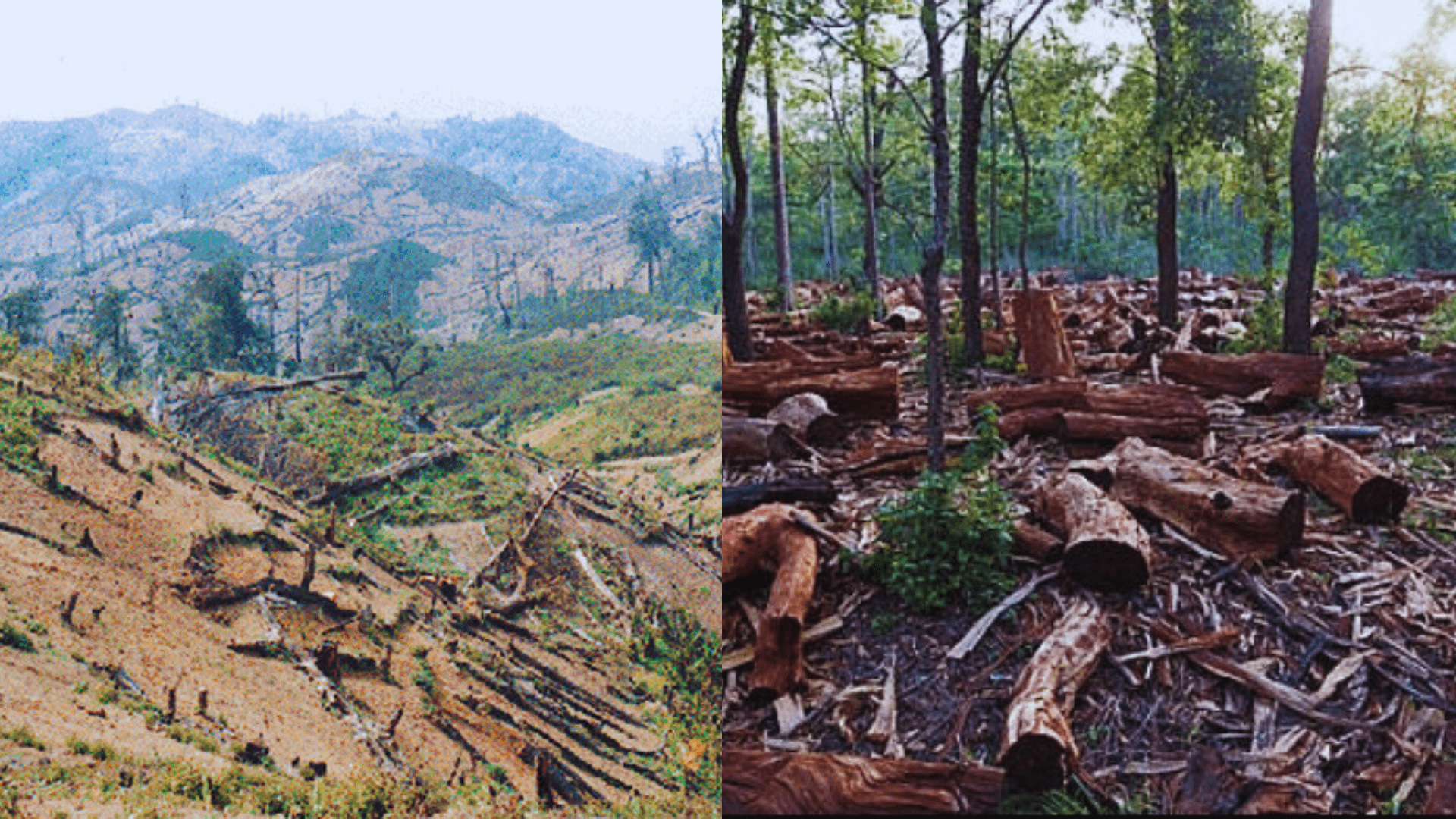
Deforestation in Nepal is not just a localized environmental issue; it extends its ramifications beyond borders, affecting neighboring countries like India. This article explores the various facets of this cross-border impact, from climate change implications and water resource management to biodiversity loss, economic ramifications, and collaborative conservation efforts.
Introduction
Deforestation in Nepal has been a growing concern, with consequences that ripple across borders. As we delve into the intricate web of ecological interconnectedness, it becomes evident that the effects of deforestation in Nepal reverberate in India, affecting everything from climate patterns to economic sectors.
Extent of Deforestation in Nepal
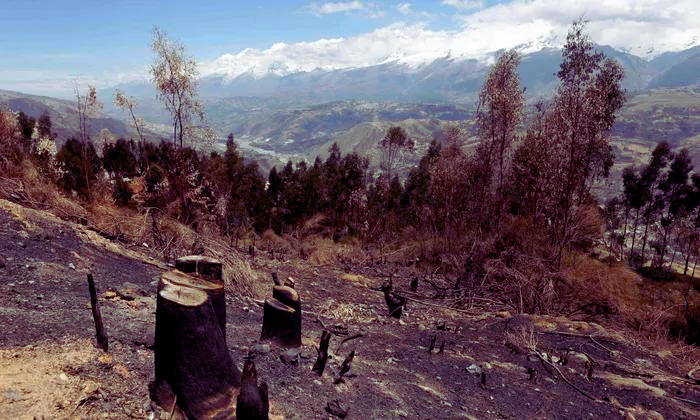

Deforestation in Nepal has reached alarming levels, with 693 deforestation alerts reported between January 13, 2024, and January 20, 2024. These alerts covered a total area of 8 hectares, with 1.4% classified as high alert areas. Massive deforestation is driven by factors like logging, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development, impacting community forests and overall forest cover. Despite Nepal’s efforts to reverse deforestation, challenges persist, as seen in the impact on biodiversity under community forest programs.
Nepal has a target to increase its forest cover to 45% by 2030, aiming to counteract the drivers of deforestation and degradation. However, addressing the extent of deforestation requires a multi-faceted approach to combat the diverse drivers and promote sustainable practices.
Ecosystem Interconnectivity
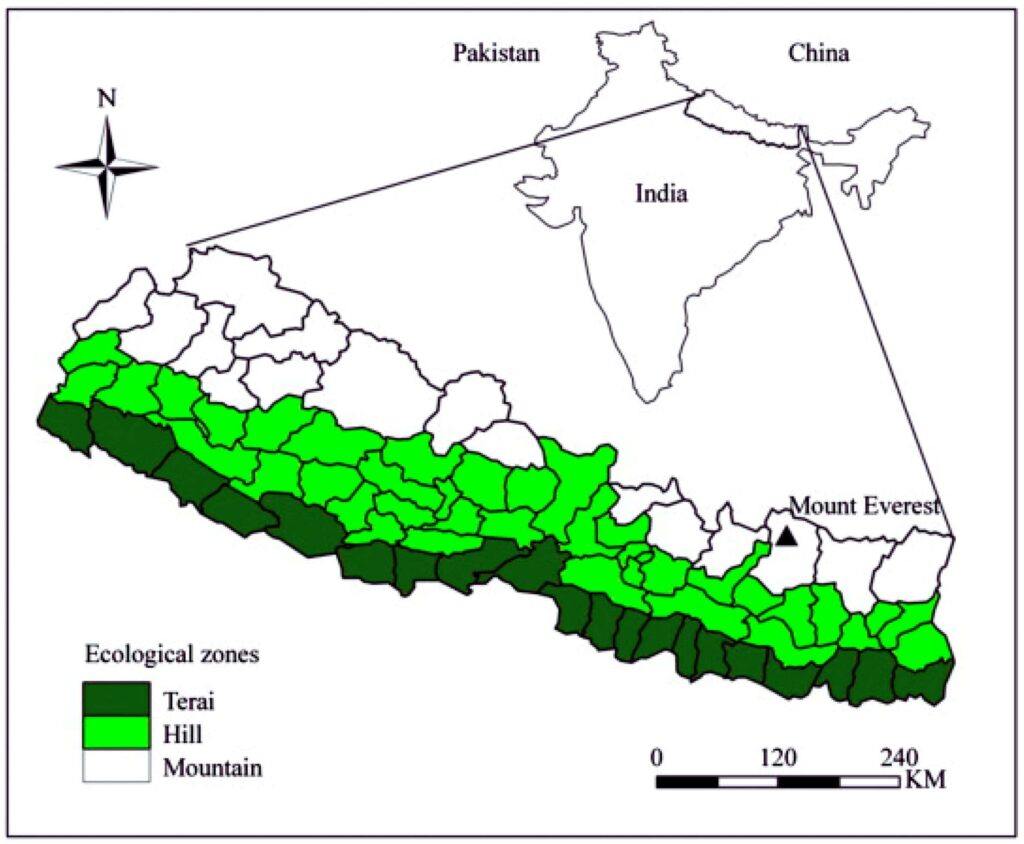
Deforestation in Nepal significantly impacts India due to the interconnectivity of ecosystems. The socio-economic transition in rural areas of Nepal has led to changes in forest management practices, affecting the ecological landscape.
The consequences of deforestation in Nepal extend beyond its borders, particularly concerning climate change and environmental governance. The degradation of tropical forests, including those in Nepal, is a global concern with implications for climate change mitigation and biodiversity conservation.
Analysis suggests that Nepal, in pursuit of economic ties with India, is sacrificing its ecology, raising concerns about environmental neglect during hydropower deals between the two countries.
Research emphasizes that anthropogenic activities, including deforestation, drive concurrent changes in the Himalayan region, affecting both forest loss and regeneration. Interventions are crucial to reducing forest loss and promoting sustainable forest management.
Cooperation between India and Nepal is essential to address unreported yet massive deforestation in the Indian Himalayas, contributing to the loss of endemic biodiversity.
Climate Change Implications

Deforestation in Nepal has far-reaching implications for India, particularly in the context of climate change. Nepal’s sacrifice of its ecology to build economic ties with India raises concerns about the neglect of environmental issues during hydropower deals between the two countries. Deforestation is a critical factor contributing to climate change, affecting weather patterns, biodiversity, and ecosystem stability.
Studies show that deforestation, biological invasion, pollution, overexploitation, fire, and mining in fragile regions, including Nepal, degrade natural ecosystems and have a significant impact on biodiversity. The consequences of deforestation extend beyond national borders, influencing global climate conditions.
In the Hindu Kush Himalaya region, of which Nepal is a part, forests play a vital role in combating climate change and mitigating its effects. Deforestation disrupts this balance, contributing to warmer and drier weather, altered precipitation patterns, and increased carbon dioxide levels.
Furthermore, the impact of forest governance and enforcement on deforestation is a crucial aspect. Factors such as illegal logging, weak forest administration, and encroachment contribute to deforestation and forest degradation in the region, affecting the overall environmental landscape.
In summary, the environmental consequences of deforestation in Nepal have cascading effects, influencing climate conditions and biodiversity not only within Nepal but also across borders, impacting India and the broader global ecosystem.
Water Resource Management

Deforestation in Nepal has notable implications for water resource management, impacting the country and its downstream neighbor, India. The construction of dams in Nepal, often associated with deforestation, has raised concerns about its impact on aquatic biodiversity. Studies, including one by the Asian Development Bank in 2018, have warned that Nepal’s dams have already influenced aquatic ecosystems, potentially affecting water quality and availability downstream, in India.
Additionally, the immediate consequences of deforestation, such as increased fuel scarcity and reduced fodder supply, can affect water resources by influencing local ecosystems and disrupting natural processes.
Water resource management is closely tied to preserving forests and vegetation cover to maintain soil productivity and water quality. Deforestation can lead to soil erosion, affecting water retention and quality both on the surface and underground.
In the context of river talks and transboundary water issues between India and Nepal, neglecting the environmental impact of such activities, especially in times of climate crisis, raises concerns about the sustainability of water resources shared between the two nations.
Biodiversity Loss and Species Migration

Biodiversity loss and species migration resulting from deforestation in Nepal have implications not only for the local environment but also for neighboring countries like India. Here’s a concise overview:
1. Forest Resurgence and Out-Migration:
In Nepal, out-migration has been linked to a positive impact on forest regeneration. The departure of people has allowed forests to recover, contributing to biodiversity conservation within Nepal’s borders.
2. Forest Loss and Fragmentation:
Deforestation and forest conversion impact ecosystems and biodiversity. The loss of natural areas can lead to fragmentation, disrupting the interconnectedness of ecosystems and affecting species migration.
3. Community Forestry Program Effects:
Nepal’s Community Forestry Program (CFP) has demonstrated mixed effects. While it has positively influenced forest management and biodiversity in some cases, the overall impact varies, with certain areas experiencing biodiversity increases due to the program.
4. Climate Change and Biodiversity Impact:
Climate change-induced factors like deforestation, pollution, and overexploitation contribute to biodiversity loss in fragile regions, affecting natural ecosystems. The consequences of these changes extend beyond national borders, impacting neighboring countries like India.
Air Quality and Health Concerns

Deforestation in Nepal contributes to air quality degradation, posing health concerns for both the local population and neighboring countries, including India. Here’s a concise overview:
1. Ambient Air Pollution in Kathmandu:
Kathmandu, Nepal, faces a significant threat from ambient air pollution, leading to potential health burdens for its residents. This pollution level has been found to reach alarming heights, impacting human health adversely.
2. Artificial Lungs Illustrating Impact:
USAID Nepal utilized artificial lungs to visually demonstrate the effects of air pollution on human health. Air pollution exposure is a critical concern, causing numerous deaths annually in Nepal and emphasizing the need for awareness and action.
3. Air Quality Plummets in the Region:
Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, and Nepal experience a decline in air quality. Forest fires, exacerbated by climate change, contribute to increased air pollution levels, impacting the health of residents across these nations.
Economic Ramifications

Deforestation in Nepal has profound economic ramifications, impacting various aspects of the country’s development and well-being:
1. Stagnant Economic Growth:
Forest degradation in Nepal has contributed to stagnant economic growth. The extensive exploitation of forests as a valuable natural resource has hindered sustainable development.
2. Global Impact on Climate:
Deforestation in Nepal contributes to warmer and drier weather globally due to the reduction in evapotranspiration, increased albedo, and elevated CO2 levels. These climatic changes have far-reaching consequences for economies and ecosystems worldwide.
3. Local Consequences on Livelihood:
Immediate consequences of deforestation include increased fuel scarcity, reduced fodder supply, and leaf-litter depletion, impacting the livelihoods of local populations. Such effects create challenges for sustenance and economic activities.
4. Impact on Smallholder Income:
Studies highlight the connection between remittance income and deforestation in Nepal. This intricate relationship underscores the need to address economic factors influencing deforestation patterns in the country.
5. Community Forestry Program:
In response to massive deforestation, Nepal has implemented the Community Forestry Program to reduce deforestation and provide support. This program reflects efforts to mitigate the economic consequences of widespread forest loss.
6. Wikipedia Overview:
Wikipedia provides a comprehensive overview of the economic impact of deforestation in Nepal, emphasizing its threat to biodiversity and the overall economic well-being of the country.
Government Policies and Conservation Efforts

Government policies and conservation efforts are pivotal in addressing deforestation challenges, especially in the context of its cross-border impacts between Nepal and India. The current forest policies in Nepal emphasize the promotion of community forestry in the mid-hills to ensure sustainable management and preservation of forest resources. Conservation practices, afforestation initiatives, and collaborative efforts contribute positively to forest cover changes in the region, demonstrating the potential effectiveness of strategic policies.
However, challenges persist, and the impact of deforestation extends beyond national borders. Wildlife-friendly infrastructure guidelines introduced in Nepal aim to reduce disruptions to wildlife, but their effectiveness may require ongoing evaluation. Collaborative initiatives involving Bhutan, India, and Nepal seek a shared vision for the conservation and sustainable development of the Eastern Himalayas, underlining the importance of regional cooperation in addressing environmental concerns.
Addressing the interconnected challenges of deforestation necessitates coordinated policies and efforts across borders, reflecting the shared responsibility of nations to preserve the environment.
Community Involvement and Sustainable Practices
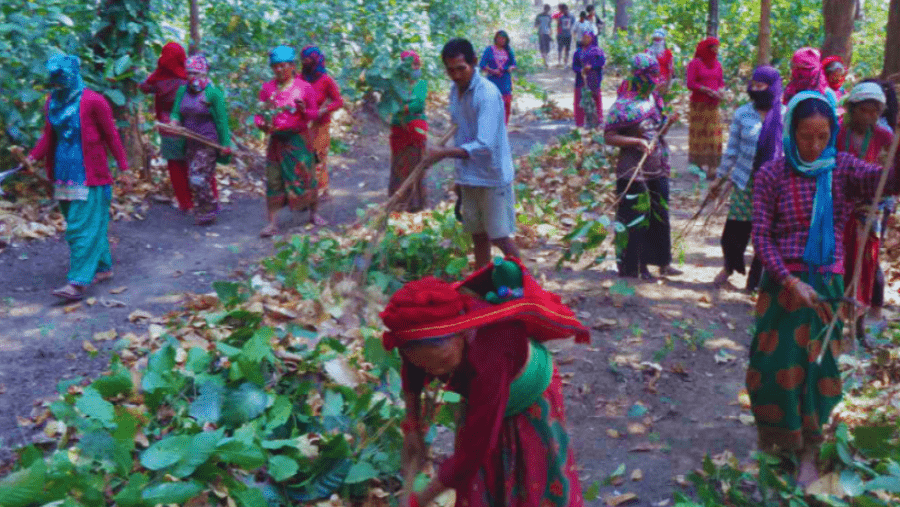

Deforestation in Nepal significantly impacts neighboring India, and community involvement along with sustainable practices plays a crucial role in addressing this issue. Several studies emphasize the interconnection between community forestry, sustainable practices, and the consequences of deforestation:
- Sustainable Forest Management: Sustainable forest management practices, such as community forestry programs, are vital for mitigating deforestation and ensuring responsible resource use.
- Immediate Consequences of Deforestation: Deforestation in Nepal has immediate consequences for local communities, leading to increased fuel scarcity, reduced fodder supply, and leaf litter.
- Impact on Agrarian-Based Economy: Unprecedented changes in socio-political, economic, and demographic factors due to deforestation have shifted Nepal’s age-old agrarian-based economy, underscoring the multifaceted consequences.
- Community Forestry Program’s Effects: The Nepal community forestry program demonstrates significant effects on forest conservation and, consequently, deforestation rates.
- Role of Community Forest Management: Studies reveal that community forest management not only reduces deforestation but also contributes to poverty reduction in Nepal, showcasing the dual impact of community involvement.
- Issues in Forest Governance: Investigating forest governance in Nepal is essential for understanding challenges and opportunities concerning sustainable practices and community involvement.
Challenges in Cross-Border Conservation

Cross-border conservation faces significant challenges, particularly concerning deforestation in Nepal impacting India. The interconnected ecosystems and wildlife movements across borders necessitate collaborative efforts to address environmental concerns. Key challenges include:
- Tigers Struggling Within Nepal: Tigers face difficulties moving safely within Nepal due to increasing isolation within protected areas, emphasizing the need for transboundary conservation efforts.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Grassroots groups are actively tackling human-wildlife conflict across the India-Nepal border, highlighting the need for coordinated efforts to address this challenge and protect both wildlife and local communities.
- Transborder Conservation Initiatives: While there are collaborative initiatives between India and Nepal to boost transborder conservation, issues like deforestation and environmental neglect need attention to ensure the effectiveness of these efforts.
- Economic Ties vs. Ecology: Concerns are raised about Nepal sacrificing its ecology for economic ties with India, highlighting the delicate balance needed between economic development and environmental conservation.
- Collaborative Conservation Efforts: Conservationists from India and Nepal are teaming up to better protect endangered species, including Bengal tigers, one-horned rhinos, and Asian elephants. Collaborative efforts are crucial to address the complex challenges of deforestation and wildlife conservation across borders.
Global Awareness and Responsibility

Nepal demonstrates a commitment to sustainable development through its national aspirations, guided by the slogan ‘Prosperous Nepal, Happy Nepali.’ The 15th Development Plan (2019/20-2023/24) actively integrates the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to address various challenges and promote global awareness and responsibility. Climate change impacts have prompted increased awareness in Nepal, as people experience the tangible effects in their daily lives. In the context of education, Nepal focuses on nurturing responsible citizens, emphasizing patriotism alongside global citizenship education to create socially conscious individuals.
India, as a prominent global player, is recognized for its soft power and influence, with a growing emphasis on responsible stewardship. India’s soft power extends to regions like Nepal, Afghanistan, and Africa, highlighting its role as a responsible democracy and market player in the international arena. As a neighboring country, India’s collaboration with Nepal on various fronts, including trade relations, signifies shared responsibilities and interconnected global awareness.
Future Projections and Predictions
Future projections and predictions indicate challenges of deforestation in Nepal affecting India. The Third Pole’s Ramesh Bhushal points out concerns that Nepal, in its pursuit of economic ties with India, is overlooking environmental issues and sacrificing its ecology. This has implications for both nations, as environmental degradation knows no borders, and actions in one region can affect neighboring areas.
Studies on global forest projections highlight potential risks. If not addressed, tropical forests, equivalent to the size of India, could be lost by 2050. Projections emphasize the urgency of taking action to prevent significant deforestation and its associated environmental impacts.
Specifically focusing on the Himalayan region shared by India and Nepal, research has delved into the determinants and policy aspects of forest degradation. This highlights the need for coordinated efforts between the two countries to address challenges arising from deforestation in this ecologically sensitive area.
Additionally, the impact of climate change on biodiversity in Nepal emphasizes the interconnectedness of ecological systems. Deforestation, along with other factors like biological invasion and pollution, degrades natural ecosystems, posing challenges that demand collaborative solutions.
Case Studies
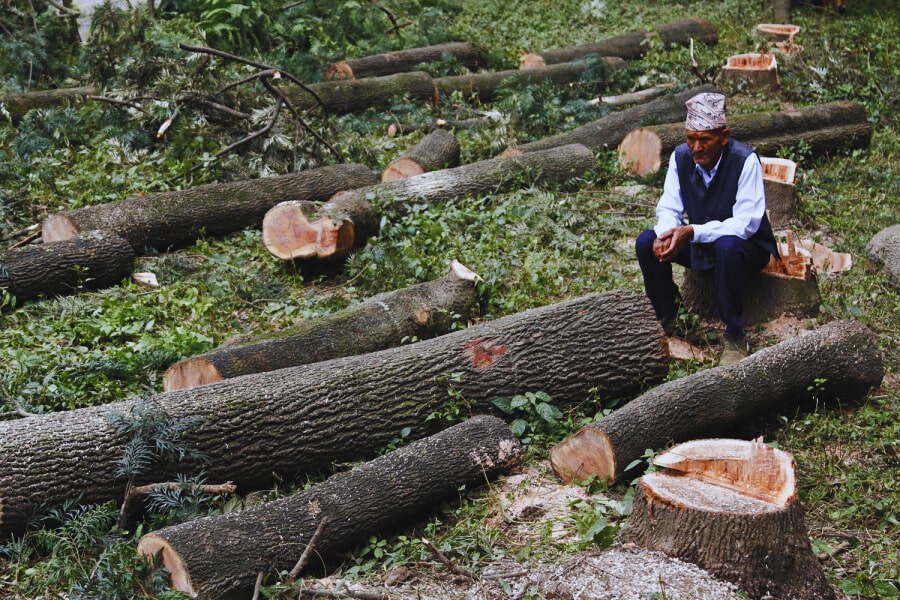

Case studies provide insights into the complex issue of deforestation in Nepal:
- Participatory Forest Management in Tarai, Nepal: A case study emphasizes the importance of involving local communities in forest management to achieve sustainable practices. It explores policy implications and impacts on forest conservation.
- Forest Resurgence Amid Out-Migration: Nepal’s case study showcases how out-migration has unintentionally contributed to a forest resurgence. By alleviating population pressure, it has helped revive forests, counteracting earlier fears of irreparable damage due to deforestation.
- Successful Reforestation in Nepal: Independent studies confirm Nepal’s success in reforestation, with forests covering 45% of the country’s land. This case study delves into the factors contributing to this positive outcome.
- Food/Fuel Context in Deforestation: A historical case study from 1983 posits that the primary cause of deforestation in Nepal is clearing forests for agriculture and fodder. It underscores the complex relationship between deforestation and the need for agricultural land.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cross-border impact of deforestation in Nepal on India is a multifaceted issue that requires immediate attention. As both nations navigate the challenges posed by climate change, water resource management, and economic interdependence, collaborative efforts are essential for a sustainable future.
Read also: Who is the Father of the Indian Constitution?
FAQs
Q. How does deforestation in Nepal affect India’s weather patterns?
Deforestation alters climate patterns in Nepal, influencing India’s monsoons, temperatures, and precipitation.
Q. What are the economic sectors in India indirectly affected by deforestation in Nepal?
Agriculture, tourism, and forestry are among the economic sectors in India impacted by deforestation in Nepal.
Q. How can local communities contribute to combating deforestation?
Local communities can contribute by engaging in sustainable practices, participating in conservation efforts, and raising awareness.
Q. What are the major challenges in cross-border conservation efforts between Nepal and India?
Challenges include differing policies, resource allocation issues, and jurisdictional complexities.
Q. Why is global awareness and responsibility crucial in addressing deforestation?
Deforestation is a global issue, and international support is essential for effective conservation, emphasizing shared responsibility.