School cancellations due to cold weather are a familiar occurrence in many regions. As temperatures plummet, schools face the challenging decision of whether to stay open or close their doors to ensure the safety of students and staff. In this article, we’ll explore the intricate factors that influence these decisions, from defining cold thresholds to the role of technology and community perspectives.
Factors Influencing School Cancellations

- Poverty Rates and School Facilities: Majority-Black schools tend to outpace others in closures, with poverty rates and the condition of school facilities playing a significant role.
- Educational Outcomes and Better Schools: It is believed that school closures can positively impact children’s educational outcomes as they may switch to better primary schools.
- Pupil/Teacher Ratio and Instructional Level: Factors associated with closures include the pupil/teacher ratio and the instructional level (elementary to high school).
- Health-related Factors and COVID-19 Risk: Health-related factors, including the risk of COVID-19, can influence school closures, reflecting the preparedness of the health system.
- Enrollment Reduction and Market Competition: Significant reductions in enrollment, underutilization, market competition from charter schools, and poor performance are commonly cited reasons for closures.
- Poor Performing Primary Schools and Educational Attainment: The closure of poor-performing primary schools can impact the educational attainment of students.
Defining the Cold Thresholds
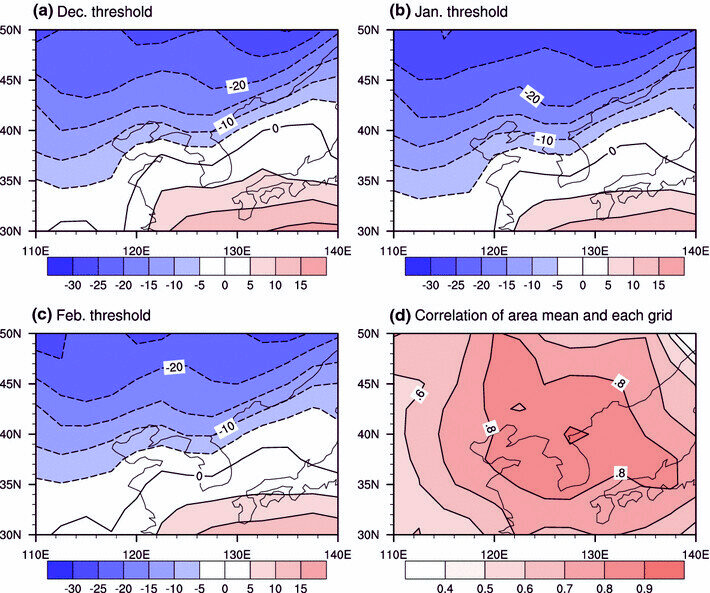
- Wind Chill Thresholds: Some school districts have a wind chill threshold to determine school closures. The decision may be based on factors like sustained temperature and wind chill, with severe cold conditions leading to closures.
- ECASD School Board Policies: ECASD school board policies define severe cold as -30°F sustained temperature and wind chill. This specific threshold guides the decision-making process for school closures in that district.
- Safety Determination: School closure decisions hinge on safety considerations for students and staff traveling to school. If it is deemed unsafe due to extreme cold, closures may be implemented.
- District Guidelines for Cold Conditions: School districts may have specific guidelines for conducting school during cold conditions. Outdoor activities might be restricted once temperatures fall below a certain level, influencing closure decisions.
- Weather-Related Closings: Districts like Glenview School provide guidelines based on weather conditions. For instance, due to a wind chill warning, all District 34 schools were closed, emphasizing the importance of considering weather factors in closure decisions.
Extreme Cold Weather

Extreme cold weather can lead to school closures as a safety measure. Factors such as dangerously low temperatures, wind chills, and the potential risk of frostbite play a crucial role in the decision-making process. Superintendents consider these factors to ensure the well-being of students and staff during extreme cold conditions. While snow and ice are common reasons for school closures, extreme cold poses its own set of challenges, prompting educational institutions to prioritize the safety of the school community. The determination to cancel school due to extreme cold varies across districts and regions, and it involves assessing the overall risk posed by the severe weather conditions.
Severe Cold Weather
Severe cold weather poses various risks to schools and early years provision. These risks include potential damage to properties, worsening existing conditions, and impacting the overall safety and well-being of students and staff. As a result, schools often implement extreme cold procedures, such as closing or modifying outdoor activities, to ensure the safety of the school community during harsh weather conditions.
Additionally, extreme cold temperatures can prompt school closures in various regions, with districts considering factors like wind chill and sustained low temperatures when making these decisions. It’s noteworthy that beyond safety concerns, research suggests that extended exposure to cold temperatures may impact learning outcomes, as seen in reduced test scores on colder school days.
Cold Weather
The decision to cancel school due to cold weather is influenced by various factors. A combination of low temperatures and wind chill often triggers school closures. Different school districts may have specific guidelines based on temperature thresholds. For example, some districts may close schools if the temperature or wind chill falls below a certain level, such as -20°F or -30°F. Additionally, considerations include the impact on transportation safety, the ability of buses to operate in extreme cold, and the well-being of students walking to school.
There is no universal standard for school closures in cold weather, and the criteria can vary widely based on local conditions and policies. Some districts closely monitor weather reports and issue closures if a wind chill warning is issued. Others consider a range of factors beyond the numerical temperature, such as the duration of extreme cold and the overall safety risks.
Moderate Cold Weather
Moderate cold weather can have various impacts on human health. As temperatures drop, individuals may experience health challenges related to the cold environment. Some notable effects include:
- Impact on Immune System: Cold weather may weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Risk of Cold-Related Illnesses: Prolonged exposure to cold conditions can lead to cold-related illnesses, such as hypothermia, due to the body’s loss of stored energy.
- Thermal Stress: Cold temperatures increase the risk of thermal stress, impacting cardiovascular health and potentially leading to mortality.
- Danger for Individuals with Chronic Conditions: Cold weather poses additional risks for individuals with chronic conditions, including cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
- Cold-Related Injuries: Exposure to cold environments may result in various cold injuries, with hypothermia being the most severe condition.
It’s crucial to take precautions, such as dressing warmly and limiting exposure in moderately cold weather, to mitigate these health risks.
Effects of Cold on Students and Staff

The temperature in educational environments can significantly impact the performance and well-being of both students and staff. Studies suggest that extreme temperatures, whether excessively cold or hot, can have adverse effects on cognitive performance and learning ability.
- Learning Ability: A 2014 study demonstrated that both excessively cold and hot temperatures directly affect students’ learning ability, potentially hindering academic performance.
- Study Time: Research indicates that frigid weather can reduce the time allocated to education for students living in cold places, affecting their study habits.
- Impact on Cognitive Performance: Cold air exposure has been shown to impair cognitive domains such as attention, speed of processing, and memory, potentially affecting the overall cognitive performance of students and staff.
- Hindrance to Learning: Multiple studies have shown that learning environments with temperatures deviating from the ideal hinder students’ ability to learn effectively.
- Exercise Participation: Lower temperatures can lead to a decrease in exercise participation among students, particularly those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds, affecting their overall health.
Understanding and maintaining optimal temperatures in educational settings are crucial for fostering a conducive environment for learning and well-being.
Case Studies on School Cancellations

Decisions regarding school cancellations due to inclement weather involve a complex process that considers various factors. Case studies provide insights into the decision-making processes in different regions.
- Central Indiana School Closures: In Central Indiana, the decision to close schools due to extreme weather involves district leaders who decide whether to hold e-learning days or give students traditional days off.
- Legal Considerations: Some argue that schools choose to close in extreme weather to avoid legal liability for potential harm to students exposed to severe conditions. This emphasizes the balance between safety and legal concerns.
- Inclement-Weather School Closures in Maryland: A case study in Maryland, USA, examines the decision-making processes behind inclement-weather school closures. This research explores the factors influencing decisions during severe winter weather conditions.
These case studies shed light on the challenges faced by educational institutions when determining whether to cancel school due to weather-related concerns.
Community Perspectives

Community perspectives on school closures due to inclement weather can vary based on local conditions and individual preferences. Some key aspects include:
- Last-Minute Decisions: The decision-making process for school closures is often last-minute, considering current and predicted weather trends. Safety concerns, especially related to dangerously cold temperatures or snow accumulation, may lead to closures or delays.
- Local Adaptations: Parents and community members might prefer school delays or closures on unusually cold days. This flexibility allows for better adaptation of personal and work schedules, particularly when it involves the safety of young children.
- Regional Variations: The criteria for canceling school due to cold weather can vary depending on the location and specific policies of the school district. Different regions may have different thresholds for what is considered too cold.
- Safety Concerns: Concerns about potential dangers, such as ice on the roads, can prompt school closures to ensure the safety of students and staff.
Technological Advances in Assessing Cold Weather Risks
Recent technological advances have significantly enhanced the assessment of cold weather risks. Here are some key developments:
- Probabilistic Forecasting: Researchers at the National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) are pioneering probabilistic tools for winter weather threats. These tools utilize new forecasting techniques, providing forecasters with a probabilistic view of cold weather events, and improving preparedness and response.
- Extreme Cold Weather Reliability Standards: The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has approved new reliability standards to enhance the grid’s reliability during extreme cold weather temperatures. These standards aim to address vulnerabilities and ensure energy security during cold weather events.
- UAS Remote Sensing: Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) are being increasingly employed for remote sensing applications in abrupt cold regions. These technologies enable risk assessment and early detection of hazards in cold-weather environments.
- Digital Tools for Prevention: Innovative digital tools like CoWEDA (Cold Weather Education and Dressing Assistant) are developed to prevent and manage cold weather-related issues. CoWEDA translates weather forecast data into appropriate clothing recommendations, improving public awareness and health outcomes.
- Smart Materials and Technologies: Ongoing research explores smart materials and technologies for mitigating challenges posed by cold weather conditions. This includes advancements in the performance and durability of concrete materials, construction processes, and structures under cold weather conditions.
Role of Social Media in School Closure Decisions

Social media threats are becoming a significant factor influencing school closure decisions, sometimes surpassing other considerations like declining COVID cases. Incidents of violent threats against schools on social media platforms are causing disruptions to in-person learning. This emerging trend underscores the impact of digital communication on educational institutions. It highlights the need for schools and authorities to navigate and respond to potential threats disseminated through social media channels. Social media’s rapid communication capabilities also play a role in crises, allowing for quick dissemination of information but simultaneously posing challenges in assessing and addressing threats promptly.
School Policies and Preparedness
To enhance school preparedness for winter emergencies, various measures and policies are recommended:
- Review Emergency Preparedness Manuals: Schools can utilize resources like the Emergency Preparedness Manual for Early Childhood Programs to create or update their winter weather plans.
- Strategies for Cold and Flu Season: As part of overall preparedness, schools should develop strategies to address cold and flu seasons. This may involve adopting best practices to ensure continuous learning during these periods, as outlined in articles like How Schools Can Prepare for Cold and Flu Season.
- Inspect HVAC Systems: Regular inspection of the Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems is crucial. Ensuring proper functioning contributes to a comfortable and safe environment, as recommended in tips provided by organizations like the Texas Association of School Boards (TASB).
- Winterize Pipes and Equipment: Preparing for winter involves winterizing pipes and major equipment, including boilers and hot water systems, to prevent issues due to freezing, as highlighted in the top tips from TASB.
- Establish Temperature Guidelines: School districts may set clear guidelines for outdoor activities during winter, considering factors like wind chill. For instance, District 97 has a policy permitting outdoor recess only when the temperature, with wind chill, is 15 degrees or higher.
- Educate and Test Systems: Schools can educate staff, students, and the community on winter weather procedures and regularly review and test systems, as advised by Ohio’s Weather Safety Awareness.
These comprehensive measures contribute to effective school policies and preparedness for winter emergencies, ensuring the safety and well-being of students and staff.
Alternative Learning Options
Educational institutions are exploring alternative learning options to adapt to extreme weather challenges and other crises. Some innovative approaches include:
- Climate-Adaptive Teaching: Schools are adopting innovative teaching methods that encourage climate adaptation in the classroom, promoting environmental awareness and resilience (UtilitiesOne).
- Alternative Method of Instruction (AMI): School districts are implementing AMI options, allowing students to learn from home during weather disruptions. This approach ensures continuous learning by leveraging online resources and remote teaching (Warren County Record).
- Online and Blended Learning: Institutions are adopting effective online and blended learning strategies, providing flexibility and continuity during crises. Blended approaches combine traditional and online methods, ensuring a manageable transition to full online instruction if needed (NCBI).
- Remote Learning Practices: The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the importance of effective remote learning practices. Schools are incorporating best practices from the physical classroom into the virtual space, creating a culture conducive to remote education (Smithsonian Magazine).
- Innovative Education Modalities: In addition to specific initiatives for climate-smart schools, there is a growing emphasis on developing and making available innovative alternative education modalities ready for deployment during crises (UNICEF).
- Global Shift to Online Learning: The COVID-19 crisis prompted a global shift to online learning. Educators worldwide transitioned to online modes overnight, emphasizing the adaptability of educational systems in the face of unforeseen challenges (SAGE Journals).
Public Reaction and Controversies
The issue of school closures has sparked significant public reactions and controversies. While some argue that school closures, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, were not a crisis and may not be solely responsible for declines in academic performance, others highlight the devastating impact on students and communities. Proponents of closures suggest that consolidating resources may lead to better educational outcomes.
In cities like Chicago, the closure of public schools has been a source of controversy and public debate. The closure of 50 public schools in Chicago a decade ago remains a contentious issue, with discussions revolving around the long-term effects on students and the educational system.
Research findings suggest that the political effects of rural school closures can vary based on ideology, with left-wing incumbents experiencing different impacts compared to their right-wing counterparts.
The debate over school closures extends beyond academic considerations, encompassing broader issues such as community disruption, resource allocation, and the long-term consequences for students and neighborhoods.
Historical Trends in School Closures
The history of school closures is marked by various instances of disruption due to public health crises and other factors. Notable historical trends include:
1. 1916 Polio Epidemic:
School closures occurred during the polio epidemic of 1916.
2. 2009 Flu Pandemic:
Schools faced closures during the 2009 flu pandemic.
3. COVID-19 Pandemic:
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a historic and widespread closing of U.S. schools in the spring of 2019-20.
- Source: The Coronavirus Spring: The Historic Closing of U.S. Schools – EdWeek
- Source: The Biggest Disruption in the History of American Education – The Atlantic
4. Recent Closure Statistics (2021–22):
In the academic year 2021–22, there were 755 school closures, including various types of schools such as regular, special education, vocational, and alternative schools.
5. Research Trends:
Scholarly research has examined trends in school closures, emphasizing empirical studies over nearly two decades.
6. Equity Concerns:
Recent research suggests that the history of school closures is inequitable, with schools serving majority-Black student populations experiencing closures between 2000 and 2018.
Tips for Parents and Students during Cold Weather

When dealing with cold weather, parents and students need to prioritize safety and well-being. Here are valuable tips to follow:
1. Layer Clothing:
Dress in layers to retain warmth. Layers can be added or removed based on temperature changes.
- Source: Nemours KidsHealth
2. Frostbite Prevention:
Protect against frostbite by ensuring children are adequately layered and covered, especially in bitter cold and snowy conditions.
- Source: Save the Children
3. Remove Drawstrings:
Prevent strangulation risks by removing drawstrings from children’s clothing. Use alternative fasteners like velcro.
- Source: PMC – NCBI
4. Head Protection:
Wear a hat to minimize heat loss, as a significant amount of body heat escapes through the head.
- Source: Caring for Kids
5. Change Wet Clothes:
Ensure children change out of wet clothes promptly to avoid discomfort and health issues.
- Source: HealthyChildren.org
6. Scheduled Breaks:
If playing outdoors, take scheduled breaks to prevent hypothermia or frostbite. Dress warmly and come indoors periodically.
- Source: Safe Kids
The Role of Local Authorities in Decision-Making
The decision-making processes for school closures involve various factors, and the role of local authorities is crucial. Here are key aspects of their involvement:
- Contested Nature: School closure decisions can be highly contested and bitter processes. Local authorities often play a central role in navigating and managing these contentious situations.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Local authorities are responsible for ensuring that the decision to close a school is based on hard, empirical evidence. This evidence should lead to a broadly supported and incontrovertible conclusion, emphasizing the importance of a rational and well-supported decision-making process.
- Balancing Trade-offs: Closing schools involves trade-offs. Local authorities must consider the potential impact on the community and students, weighing the benefits of slowing a pandemic against the social and educational consequences of closures.
- Final Determination: School boards, often representing local authorities, typically have the authority to make the final determination regarding school closings. Their decisions impact students, communities, and various stakeholders.
- Public Health Considerations: The closure decisions require a delicate balance between local public health concerns and broader societal considerations. Public health and school officials collaborate to make decisions that prioritize both local and broader concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision to cancel school due to cold weather is a complex interplay of various factors. From defining cold thresholds to understanding community perspectives and leveraging technological advances, authorities must balance safety and education. Navigating the challenges of extreme weather requires a holistic approach that prioritizes the well-being of students and staff.
Read also: How to Watch Chiefs Games?
FAQs – Unveiling the Cold Truth
Q: How cold does it have to be for schools to close?
The threshold varies, but extremely cold weather, severe cold conditions, and even moderate cold considering factors like wind speed, can lead to school closures.
Q: Are there alternatives to traditional schools during closures?
Yes, with technological advances, schools can implement remote learning strategies to ensure educational continuity during weather disruptions.
Q: How do local authorities collaborate with meteorological agencies?
Local authorities work closely with meteorological agencies to receive real-time data and forecasts, aiding in proactive decision-making.
Q: Why do school closure decisions sometimes spark controversies?
Balancing safety and education often leads to debates. Authorities must carefully navigate public opinions, considering the unique challenges of each situation.
Q: What can parents and students do to prepare for cold weather disruptions?
Dressing appropriately, staying informed about school communication, and being prepared for potential closures are essential steps for parents and students.